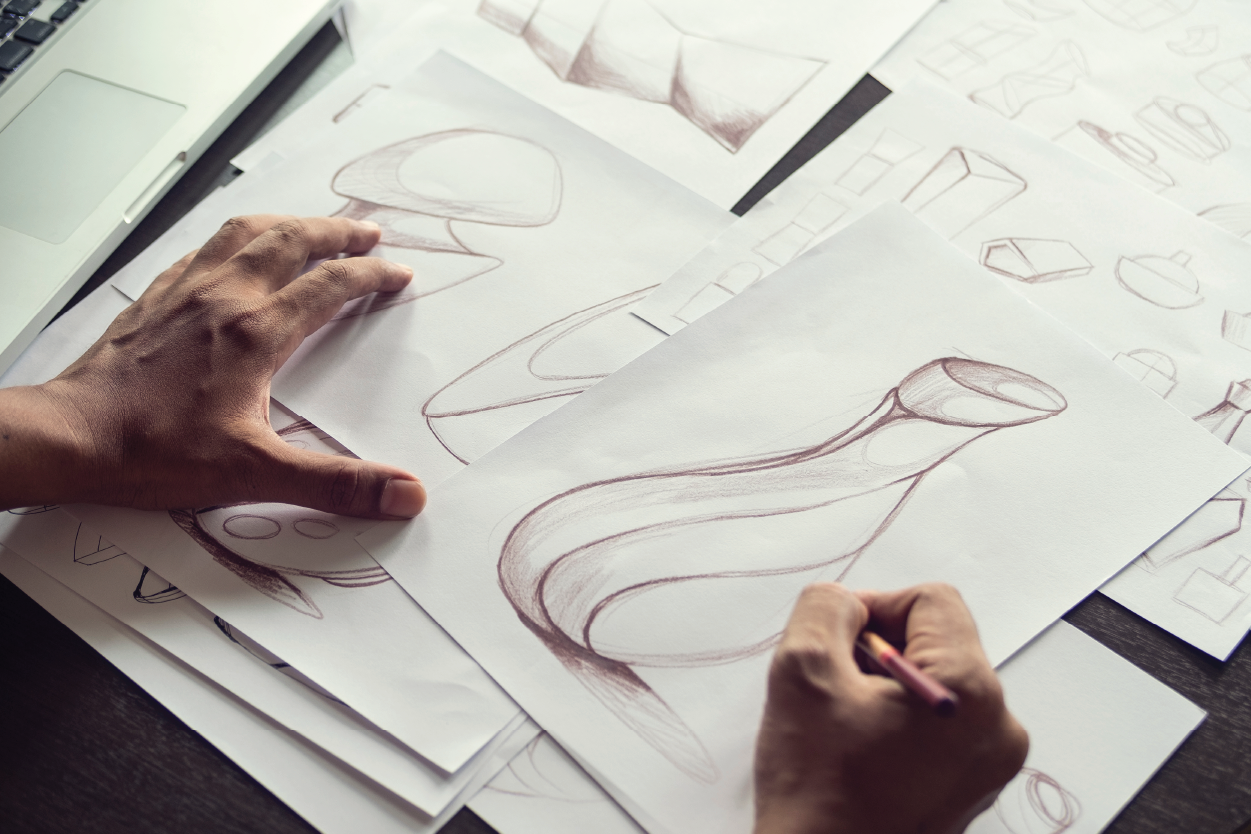
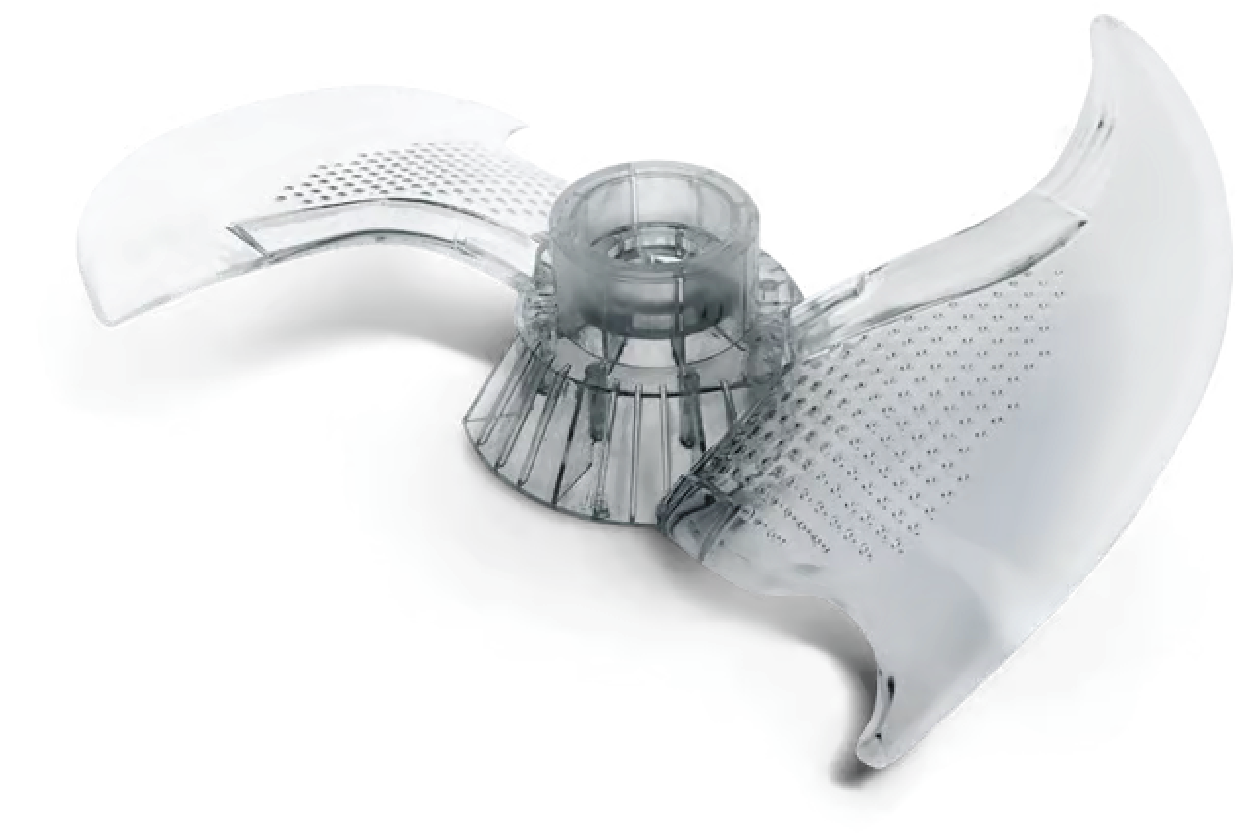
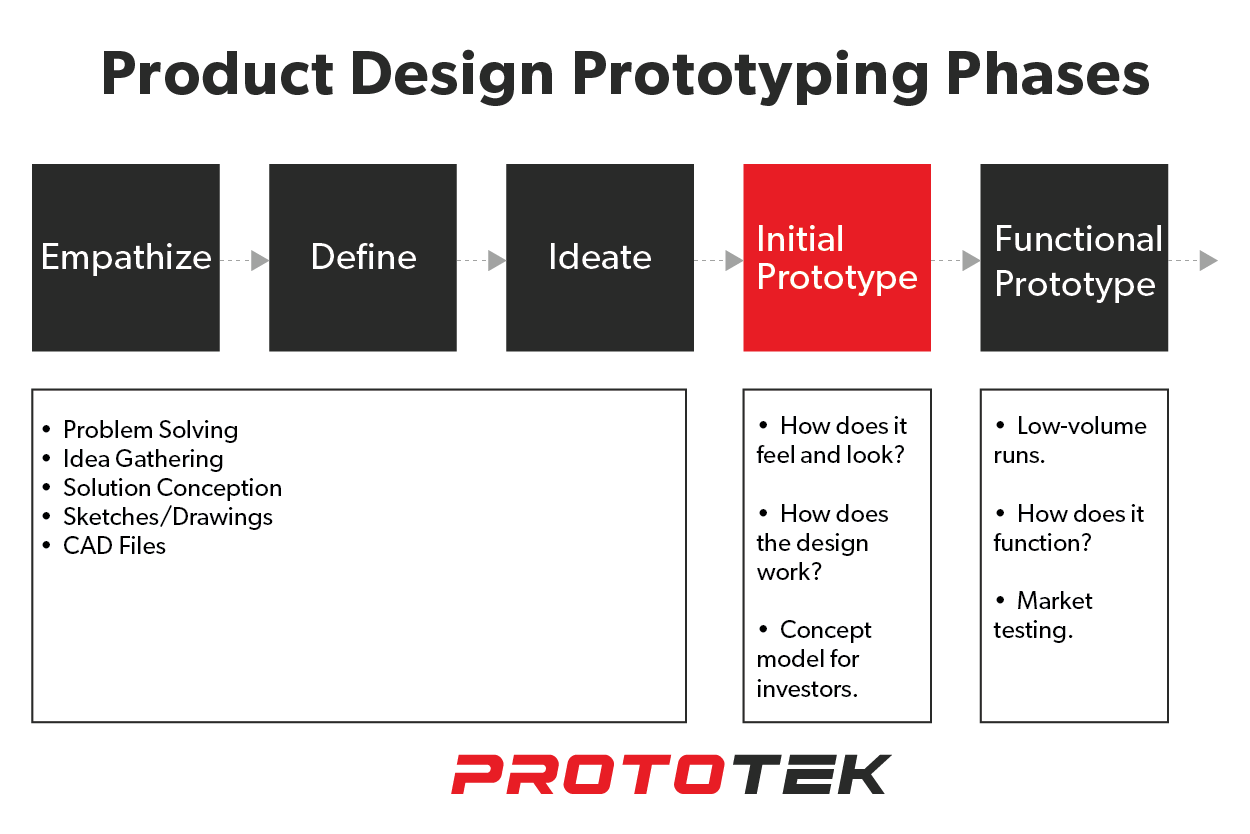
The initial prototyping phase is crucial in product development, laying the groundwork for a successful final product. At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we recognize the significance of this phase and are here to assist you through it. In this blog post, we will discuss the key elements you must understand to navigate the initial prototyping phase confidently and efficiently.
What is initial prototyping?
An initial prototype is an early-stage model or sample that showcases the design of a product or concept. This important preliminary step enables teams to test the prototype, collect feedback, and make iterative improvements before proceeding with functional prototypes and eventual full-scale development. The type of manufacturing used to create the prototype depends on the project’s specific needs and objectives and the level of detail required for effective validation and refinement. Utilizing prototypes increases the likelihood of project success.
What are the ideal manufacturing processes for the initial prototyping phase?
When it comes to prototyping, choosing the right manufacturing processes can significantly impact the success of your project. Therefore, selecting methods that enable you to bring your design to life quickly and cost-effectively is essential during the initial prototyping phase.
At Prototek, we recommend considering several key manufacturing processes that are particularly well-suited for early-stage prototyping:
Additive Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing technologies, including fused filament fabrication (FFF), multi-jet fusion (MJF), stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS), are particularly well-suited for producing functional prototypes that feature complex and intricate geometries. Each additive manufacturing process utilizes different methods to create parts layer by layer, allowing for high design flexibility and customization.
Fused filament fabrication (FFF) involves extruding thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle, building the object layer by layer. This process is cost-effective and ideal for quickly producing prototypes.
On the other hand, multi-jet fusion (MJF) uses jets to deposit a binding agent onto layers of powdered material, followed by the application of heat to fuse the particles. This technology is known for producing highly detailed parts with superior mechanical properties.
Stereolithography (SLA) employs a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers, creating prototypes with exceptional surface finish and fine detail. This technique is particularly advantageous for applications where precision is critical.
Selective laser sintering (SLS) utilizes a laser to sinter powdered material, binding it together to create robust and functional parts. This method accommodates various materials, including plastics and metals, making it versatile for multiple applications.
These additive manufacturing processes facilitate rapid design iterations and eliminate much of the time and expense associated with traditional tooling. As a result, they are rapidly becoming essential tools in product development, allowing designers and engineers to test and refine their ideas more efficiently.
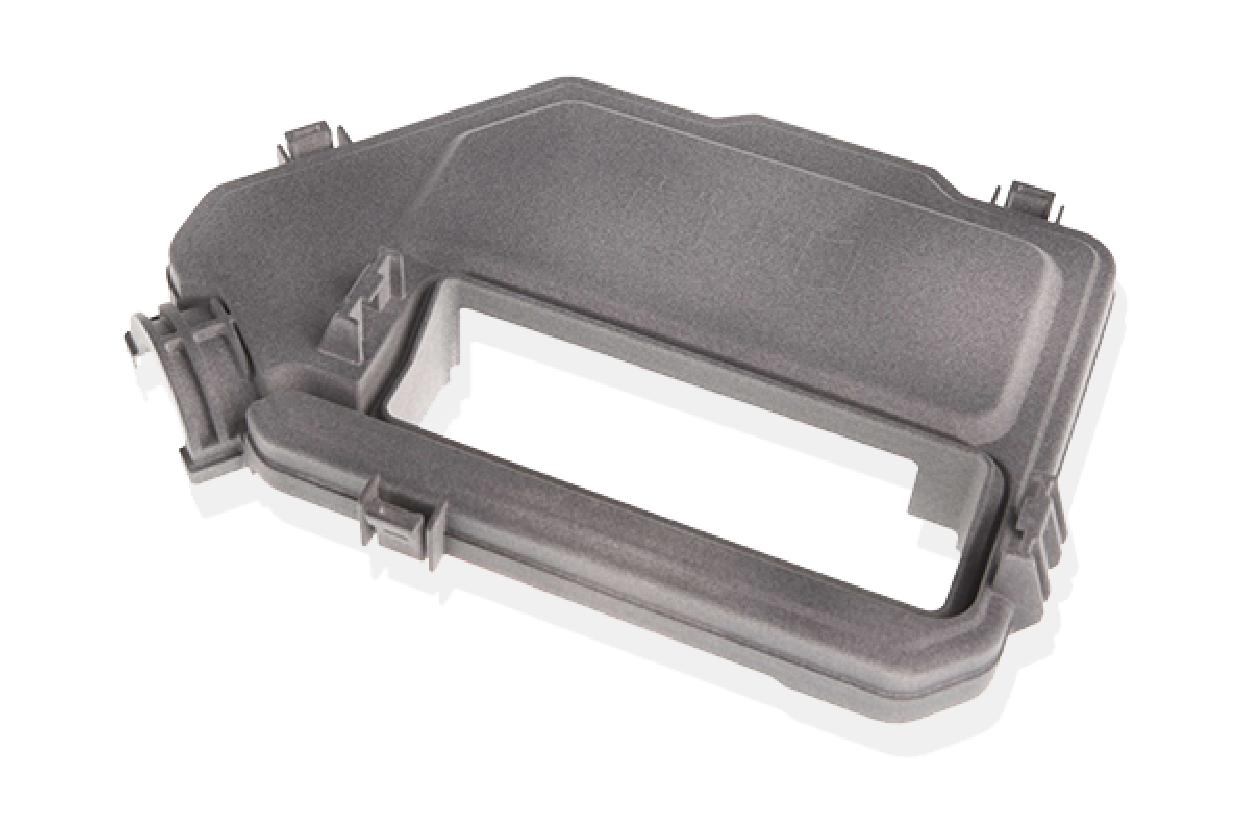

Bridging the gap between initial prototyping and functional prototyping.
In product development, the journey from concept to a market-ready product involves several critical milestones. Two of the most essential steps in this process are initial prototyping and functional prototyping. While both are important, understanding their differences can help streamline your product development journey.
Initial prototyping focuses on quickly validating the core concept and design. These early-stage prototypes are often low-fidelity, allowing you to test the fundamental idea, gather feedback, and refine your direction. In contrast, functional prototyping creates a more advanced working model that resembles the final product.
Methods such as additive manufacturing, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and low-volume casting can effectively bridge the gap between these stages. Whether you’re looking to validate your design, test product functionality, or prepare for manufacturing, each step is crucial in bringing your product to market.
Are you ready to start your project?
FAQs
Rapid prototyping is a highly efficient and cost-effective process involving quickly creating physical models or parts. This is achieved through additive manufacturing technologies, which allow for the layering of materials to build intricate designs. These techniques enable designers and engineers to quickly test and iterate their concepts, leading to faster innovation and product development.
At Prototek, we guide you through the entire prototype manufacturing process. From design to production, our team of experts gives feedback and leverages the latest technologies to bring your ideas to life quickly and cost-effectively. Let us help you turn your concept into a tangible reality.
Utilizing additive manufacturing techniques during the initial phase of prototyping can significantly reduce both the time and costs involved in the development process. This technology allows for rapid production of parts and components, enabling designers and engineers to quickly create, test, and refine their concepts without the lengthy lead times associated with traditional manufacturing methods. As a result, teams can iterate on their designs more efficiently, ultimately accelerating the overall product development timeline while minimizing financial investments in materials and tools.










