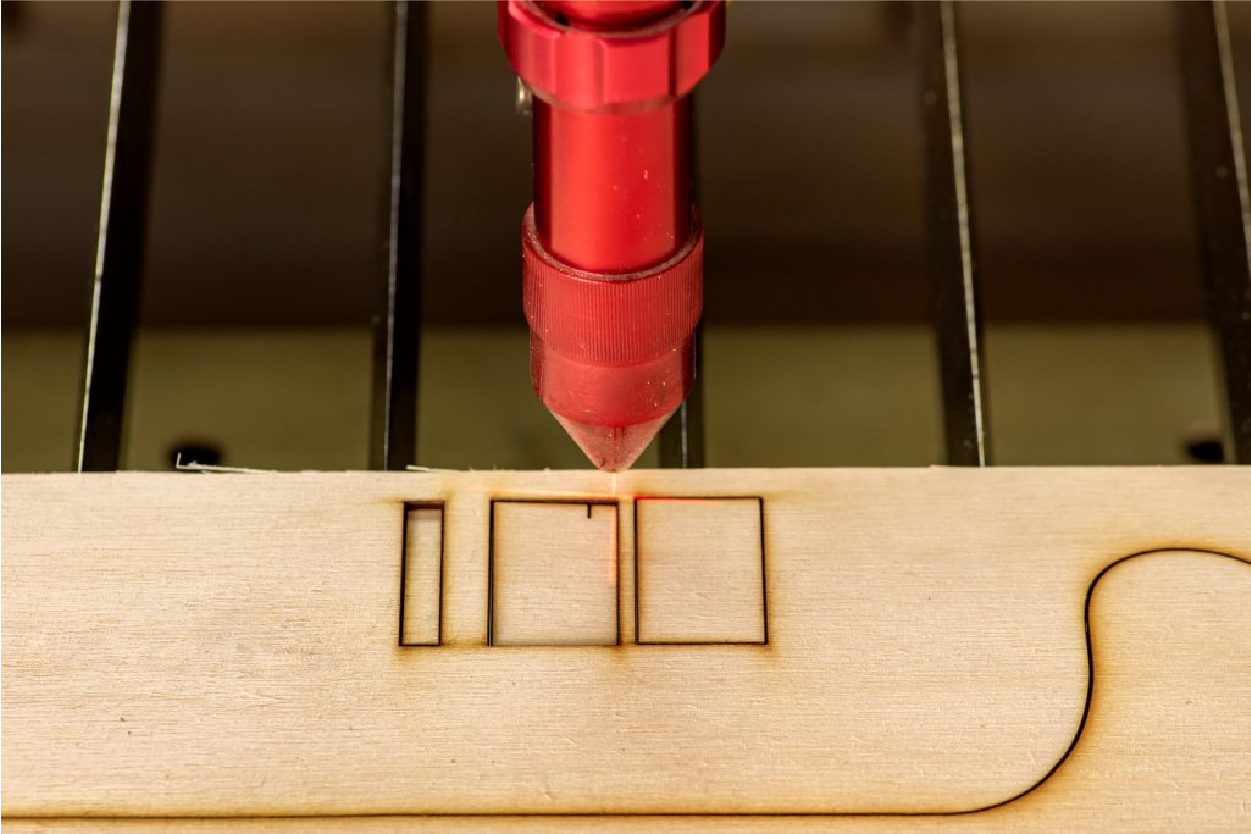
Laser cutting is an exact and efficient manufacturing process that utilizes a focused beam of high-energy laser light to cut through a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. Moreover, this advanced technology enables cutting intricate and complex designs with exceptional accuracy and speed, making it a popular choice for various industrial and commercial applications. At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we leverage laser cutting to deliver outstanding client results. Therefore, we help them bring their ideas to life with unparalleled precision and efficiency.
How does laser cutting work?
Laser cutting is an exact and efficient manufacturing process that involves using a concentrated beam of light to cut through a wide range of materials. First, the focused laser beam, commonly emitted by a carbon dioxide or fiber laser, is directed onto the workpiece, causing the material to either melt or vaporize as it traverses the desired cutting path. As a result, this intricate process allows for the creation of incredibly detailed and complex designs with exceptional accuracy and speed. Consequently, it has become preferred in aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics because it delivers high-quality, intricate components with great precision.
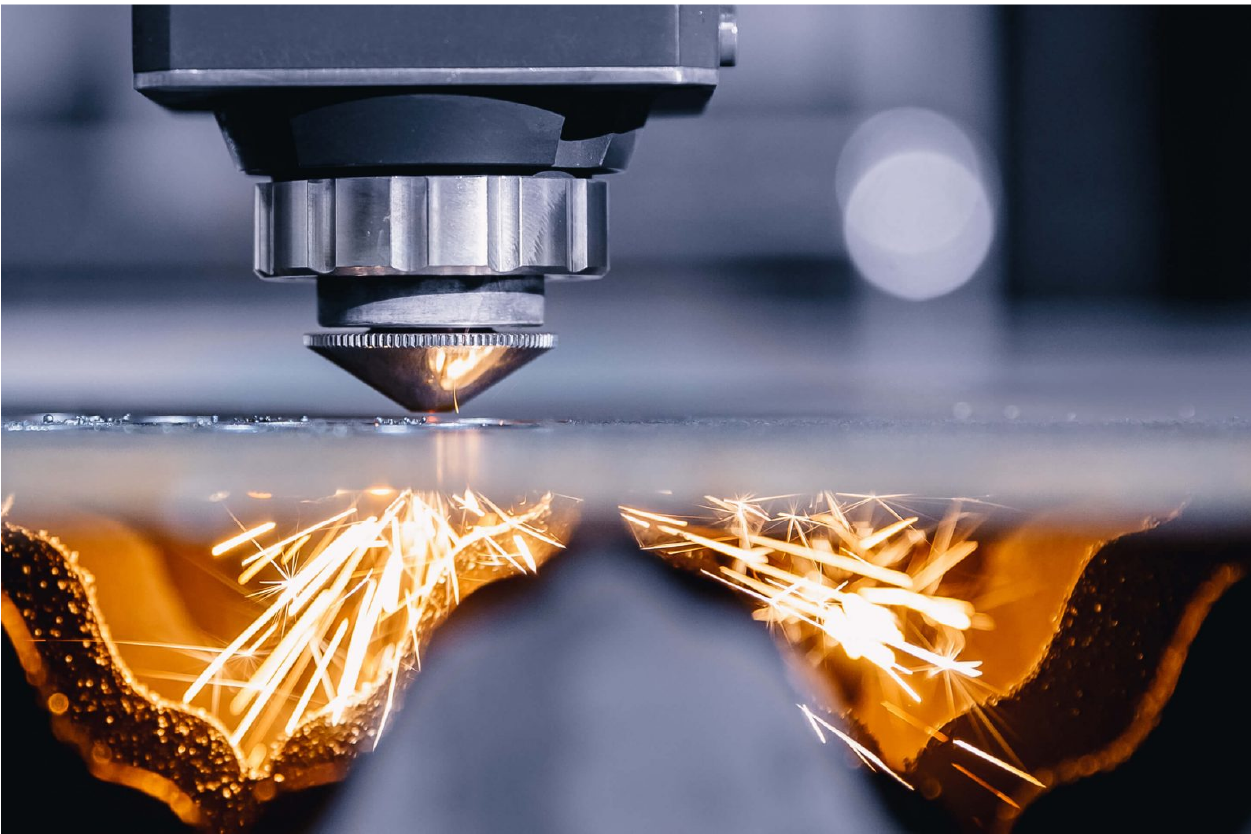

Types of Laser Cutters
CO2 Laser Cutter
CO2 laser cutters use a focused beam of high-energy infrared light to cut through various materials precisely by generating a laser beam by exciting a mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and other gases within a sealed chamber. This excited gas mixture produces intense laser light, which is then directed and focused using mirrors and lenses onto the cut material. The concentrated laser energy melts and vaporizes the material, allowing for clean, accurate cuts. Furthermore, CO2 laser cutters are versatile tools capable of cutting materials like acrylic, wood, fabric, and thin metals with exceptional speed and precision.
Crystal Laser Cutters
Crystal laser cutters use a focused laser beam to cut or engrave various materials precisely. Generating the laser beam excites the electrons in a crystal, such as a ruby or neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) crystal. As the excited electrons return to their normal state, they emit amplified photons to create a powerful, coherent laser beam. Subsequently, the machine focuses and directs the laser beam by using mirrors and lenses to cut or etch the desired pattern into the material.
Fiber Laser Cutter
Fiber laser cutters employ a highly focused beam of light to cut through a variety of materials precisely. The laser beam is generated by exciting a fiber-optic cable doped with rare-earth elements, typically ytterbium or neodymium. Consequently, this process creates an intense, collimated beam that can be directed and controlled to cut intricate patterns with exceptional accuracy and speed. Fiber laser technology offers superior beam quality, as well as energy efficiency and reliability, making it a versatile and popular choice for industrial cutting applications.
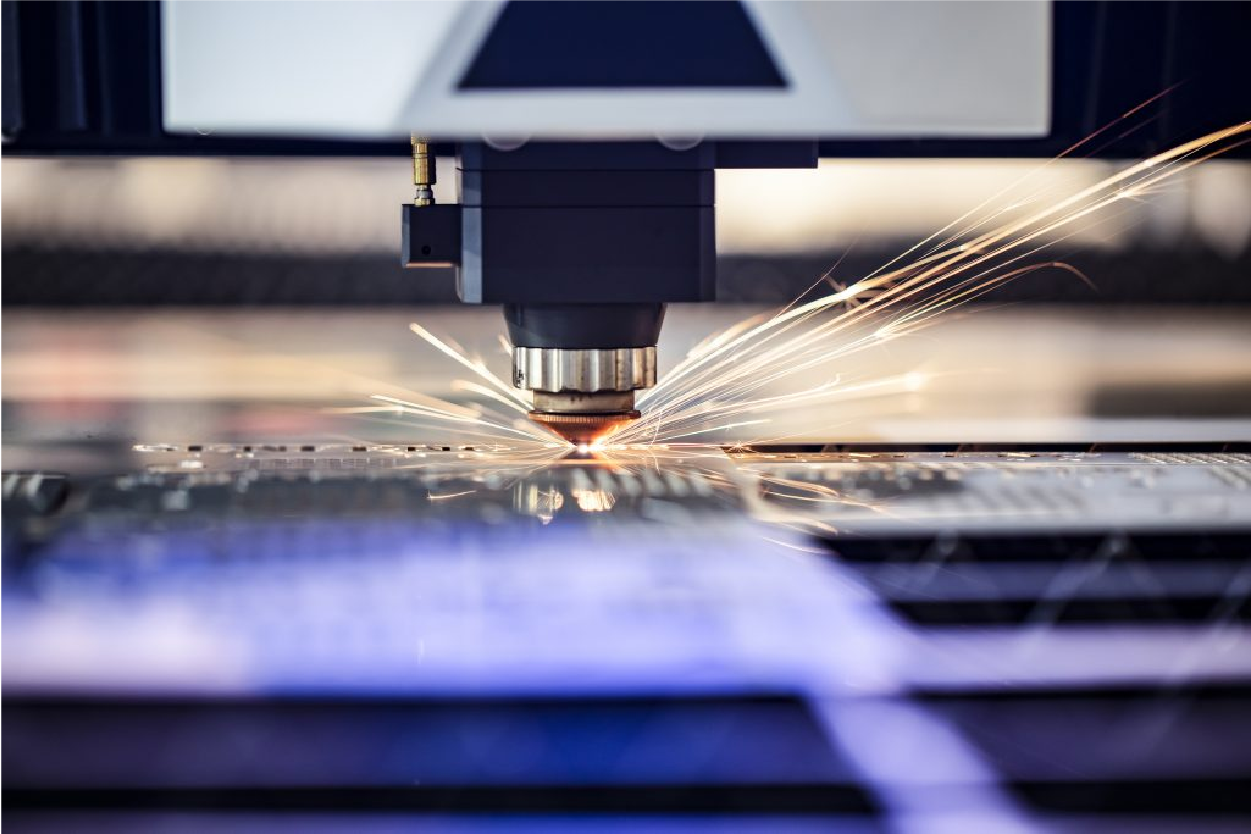

Why use a laser cutter?
Additionally, laser cutting offers several advantages over other cutting methods:
1. Faster processing and production times
2. Minimal warping
3. Greater accuracy compared to flame or plasma cutting
4. More parts per sheet of material due to the laser beam’s small cutting diameter (kerf)
5. Suitable for thin materials, but thicker and denser materials may be cut by replacing the collimating lens to change the laser’s focal point.
Furthermore, it has several advantages over flame, plasma, and waterjet cutting. The laser’s tightly focused heat application requires less power and reduces the material’s heat-affected zone (HAZ). Many high-end industrial laser cutting machines are accurate to 10 micrometers and have a repeatability of 5 micrometers. Moreover, lasers can affordably cut and etch various materials, including non-metallic materials that typically cannot be cut by flame or plasma processes.
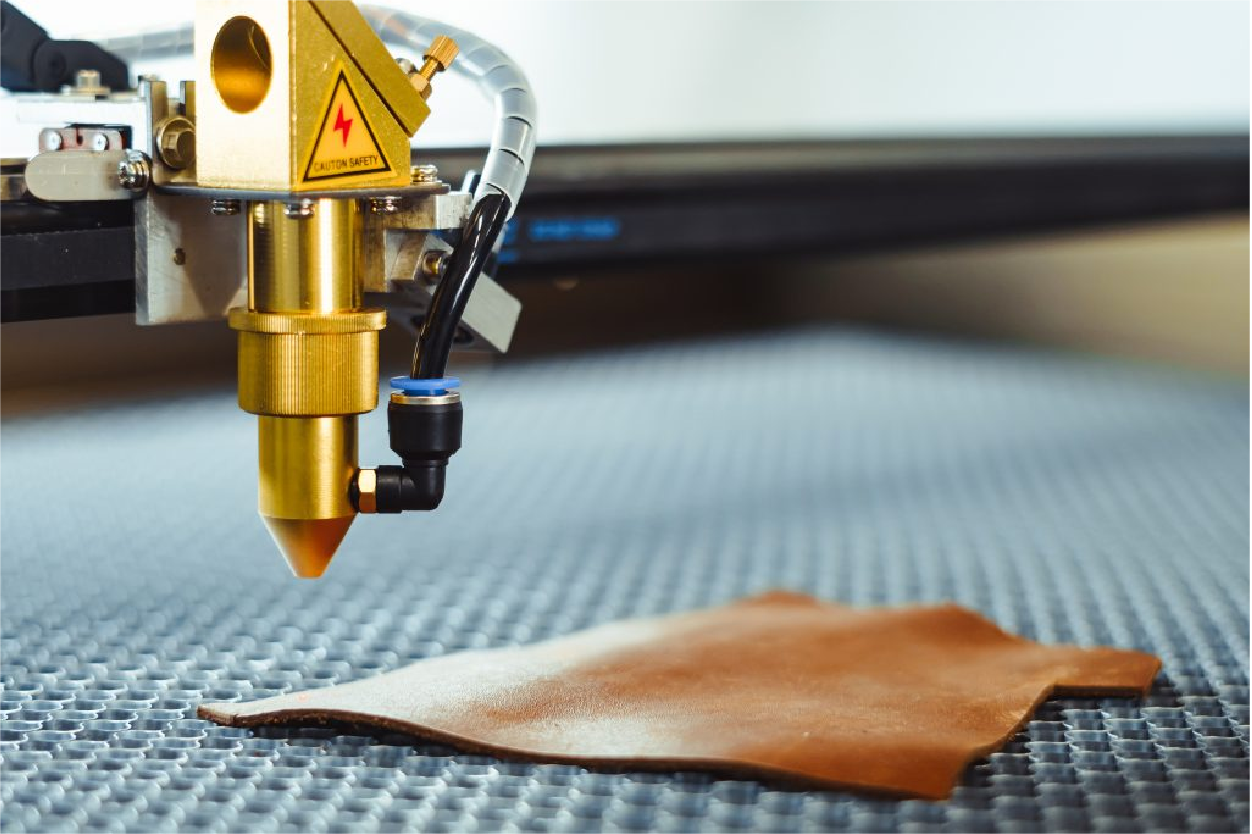

Is laser cutting right for my parts?
Laser cutting is an exact and efficient method for fabricating sheet metal parts. At Prototek, our state-of-the-art cutting capabilities allow us to produce complex, intricate designs with exceptional accuracy and speed. Whether you require prototypes or production runs, our team can work closely with you to determine if it is the optimal manufacturing process for your specific parts and needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and explore how our sheet metal laser-cutting services can benefit your business.
Are you ready to start your project?
FAQs
Laser cutting is an accurate and efficient manufacturing process that utilizes a focused laser beam to cut through various materials, allowing for intricate designs and customization.
It is a precise and efficient manufacturing process that employs a high-energy laser beam to cut through various materials. The laser beam focuses on the workpiece, melting or vaporizing the material along the desired cut path. This results in clean, accurate cuts with minimal waste.
It can precisely cut various materials, such as metals, plastics, wood, and acrylic. Additionally, it can cut more, making it a versatile manufacturing process.
It is a versatile manufacturing process utilized across diverse industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical, and more. It enables precise, efficient, and cost-effective part production.