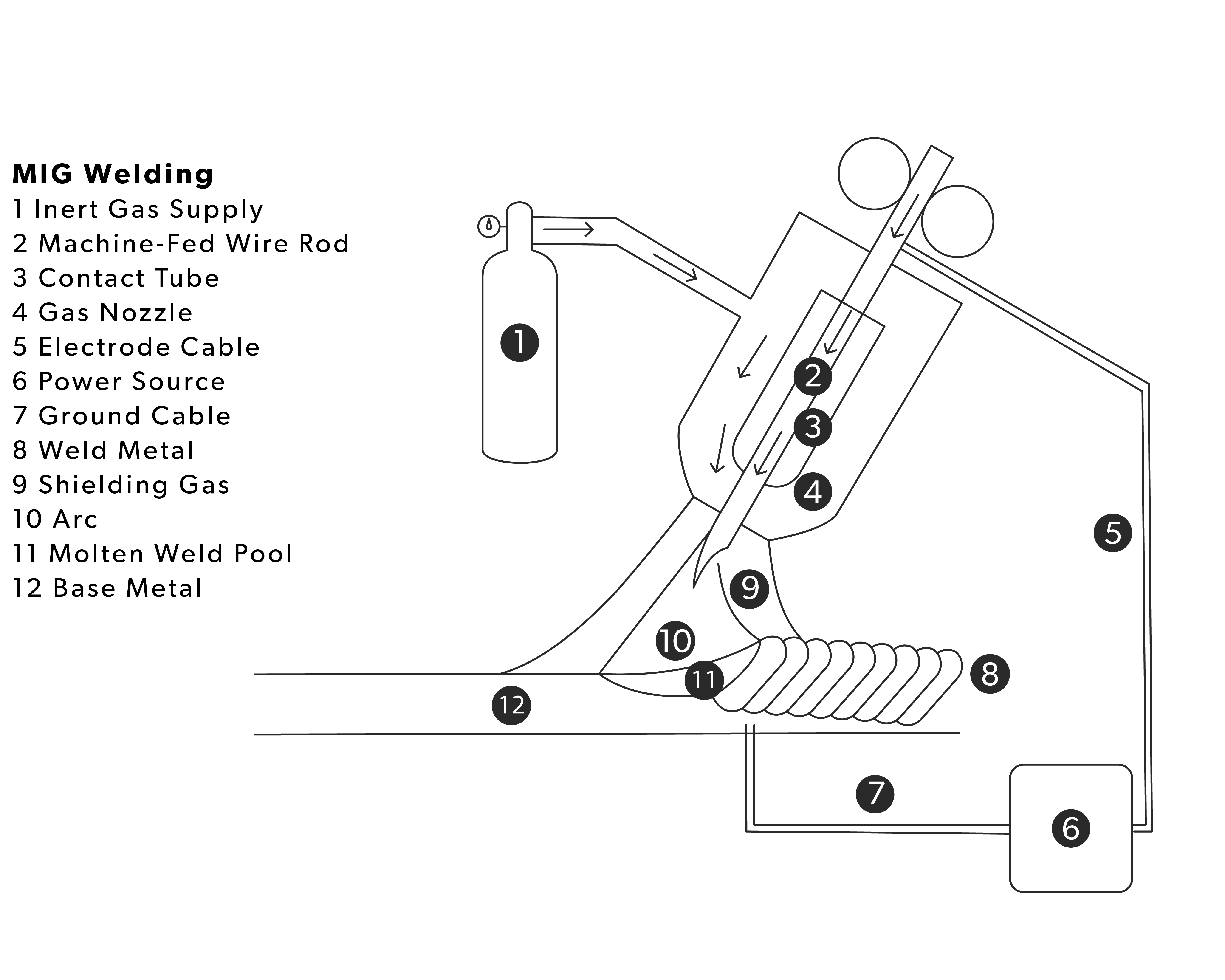
Metal inert gas (MIG) welding, also known as gas metal arc welding (GMAW), is a pivotal process in manufacturing and fabrication. This method involves a continuously fed wire electrode and shielding gas to produce solid, high-quality welds.
The process uses an electric arc between the wire electrode and the workpiece. A shielding gas, typically a mix of argon and carbon dioxide, protects the weld area from contamination.
MIG welding is renowned for its versatility. It results in a clean and consistent weld and can handle many materials. These materials include steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, making it a practical choice for many applications.
MIG welding is a highly productive and efficient welding method. It has become the ideal choice for many manufacturing and fabrication operations. Its versatility and user-friendly nature have established this process as an essential tool for the modern metalworker.
How does MIG welding work?
Inert gas MIG welding is a highly versatile and commonly used method across various industries. Due to its user-friendly nature and adaptability, it is particularly beneficial for beginners. These are the necessary tools for MIG welding:
Tools:
- Angle Grinder
- Materials for Welding
- MIG Welding Machine
- Shielding Gas
- Welding Clamps
- Welding Gloves
- Welding Gun
- Welding Helmut
- Welding Wires
Other Helpful Tools:
- Chipping hammer
- MIG pliers
- Speed square
- Welding magnets
- Wire brush
Mastering MIG welding is crucial whether you’re working on a DIY project or pursuing a career in manufacturing. You must follow these steps for successful welding, from setting up your welding station to allowing the weld to cool completely.
Set Up Your Welding Station
First, set up your welding station in a well-ventilated area. Gather and organize all the tools you’ll need. Ensure that the area is clean and free of flammable materials.
Prepare the Metal Surfaces
Thoroughly clean the metal surfaces you plan to weld to remove rust, oil, paint, or other contaminants. Subsequently, it will ensure a solid and clean weld.
Adjust Your MIG Welder Settings
Properly set your MIG welder’s voltage, wire feed speed, and shielding gas flow rate. These will depend on the specific requirements of the metal you are welding.
Strike the Arc and Begin Welding
Once you have set up your welding station and prepared the metal surfaces, securely hold the MIG gun. Determine the arc length, which will be the appropriate angle and distance from the workpiece. Initiate the welding arc to begin the welding process.
Maintain Consistent Travel Speed
Maintain a steady travel speed and keep a consistent distance between the MIG welding gun and the workpiece. It’s also essential to create a uniform weld bead of filler metal.
Finish Strong with a Proper Weld
Watch the weld pool closely to ensure the molten metals shape correctly. The weld must penetrate the base metals to create a strong and lasting joint.
Allow the Weld to Cool Completely
After finishing the weld, allow it to cool naturally without any external assistance. This step will ensure the integrity of the metal joint.
What materials can be MIG welded?
The application of the MIG weld process to the following materials:
Aluminum
It is an excellent welding technique for aluminum parts and assemblies, providing a clean, high-quality finish.
Carbon Steel
This welding technique is standard for joining carbon steel components, from thin sheet metal to thicker structural steel.
Mild Steel
MIG welding is well-suited for joining mild steel materials. Making it a practical choice for many general fabrication needs.
Stainless Steel
This welding process produces solid and corrosion-resistant joints when applied to weld different grades of stainless steel.
Steel Alloys
The process can handle welding alloy steels, including those used in machinery, automotive, and other industrial applications.
MIG welding has become an essential tool in the manufacturing and fabrication industries. Gas metal inert gas MIG welding can handle this diverse range of metals. By leveraging this versatile method, businesses can confidently tackle various welding projects.
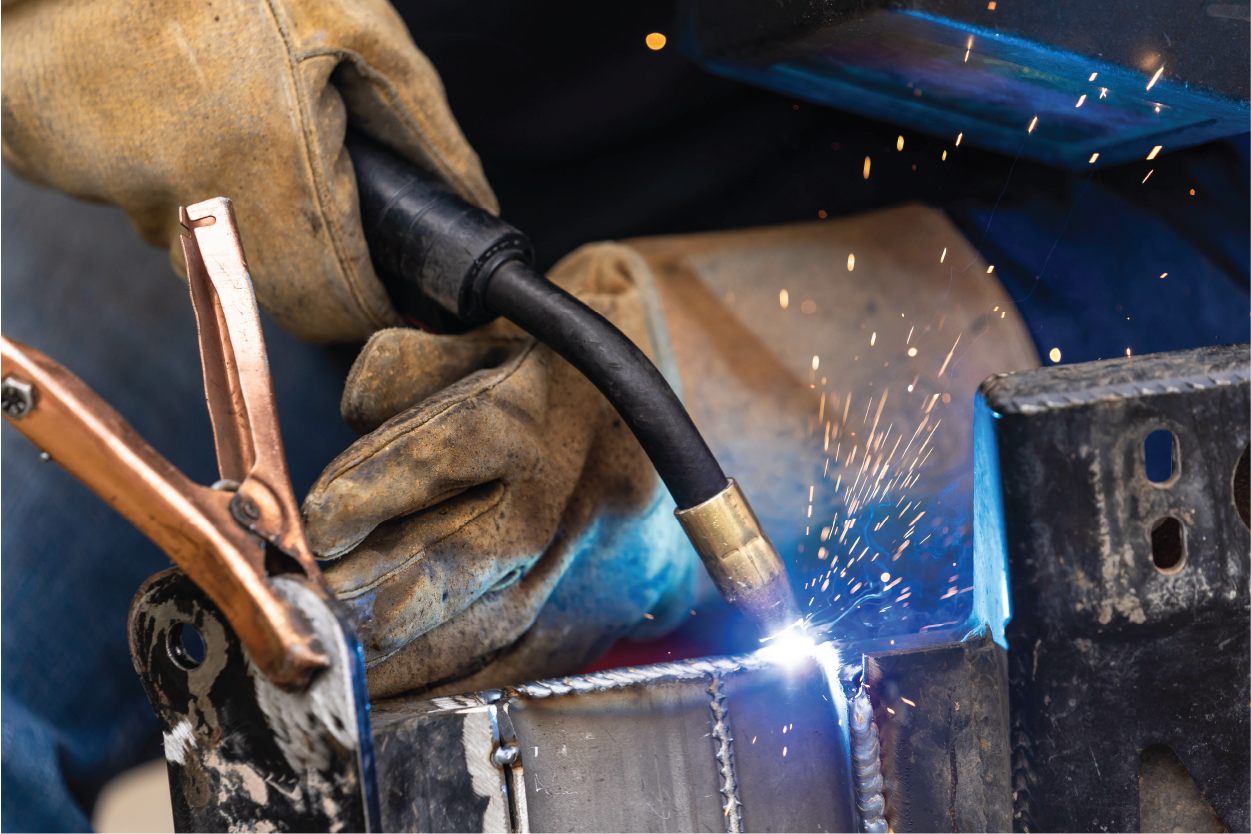

What are the benefits of MIG welding?
MIG welding, or metal inert gas welding, is an incredibly versatile technique in various manufacturing and fabrication applications. We leverage the benefits of this type of weld, ensuring the delivery of high-quality, cost-effective solutions. In this section, we will delve into the critical advantages of MIG welding and why it remains a go-to choice for many industries.
One of the most appealing aspects of MIG welding is its relative simplicity and ease of learning. This accessibility makes it a technique that both experienced welders and newcomers to the craft can confidently master. The semi-automatic process allows for consistent, high-quality welds, instilling confidence in the learner.
In addition, MIG welding is a fast and efficient process. It allows for higher welding speeds and deposition rates than other welding methods. Increasing productivity and reducing manufacturing lead times. This efficiency instills a sense of accomplishment in the welder.
MIG welding is a versatile process for various metals, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and more. This adaptability enables us to undertake a diverse range of projects while meeting the unique needs of our customers.
Another significant advantage of MIG welding is the solid, high-quality welds it produces. With minimal spatter and a smooth, uniform appearance, these welds testify to the process’s reliability. A shielding gas protects the weld from contamination, guaranteeing optimal joint strength and durability.
At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we leverage the benefits of MIG welding to deliver exceptional results for our clients. You can rely on us to provide high-quality, cost-effective solutions tailored to your requirements.

Why choose MIG welding for your project?
MIG welding is a flexible and effective option for many manufacturing projects. It provides high-quality welds, fast production rates, and is easy to use. Making it a popular choice in various industries. You can trust that we will deliver consistent, high-quality results for your project.
CNC Machine Shop Services
Prototek offers state-of-the-art CNC machining services to meet your precise manufacturing needs. Our skilled technicians utilize the latest CNC technology to deliver high-quality components with unparalleled precision and efficiency—Trust Prototek for all your CNC machining requirements.
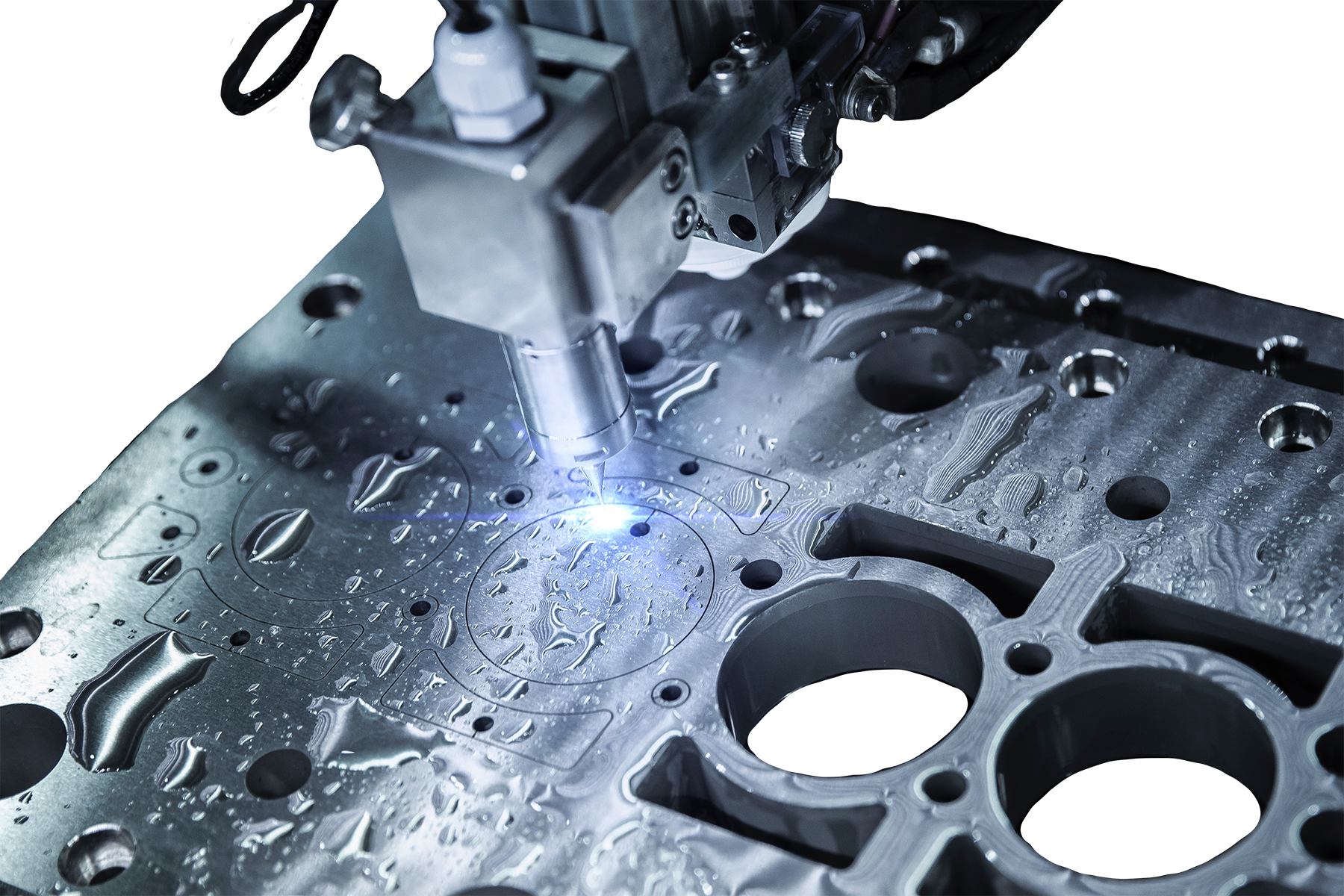

Sheet Metal Fabrication Services
At Prototek, we offer comprehensive sheet metal fabrication services to meet your manufacturing needs. Our skilled team utilizes the latest technology and techniques to deliver high-quality, precision-engineered components. From prototyping to production, trust Prototek to bring your ideas to life.
FAQs
Due to its versatility and efficiency, it is a common type of weld in the automotive, construction, fabrication, and manufacturing industries.
It is a popular arc welding process utilizing a continuous solid wire electrode and an inert shielding gas to join metal parts. It provides high-quality, efficient, and versatile welding solutions.
Due to its versatility and efficiency, this process is a common wound in the automotive, construction, fabrication, and manufacturing industries.










