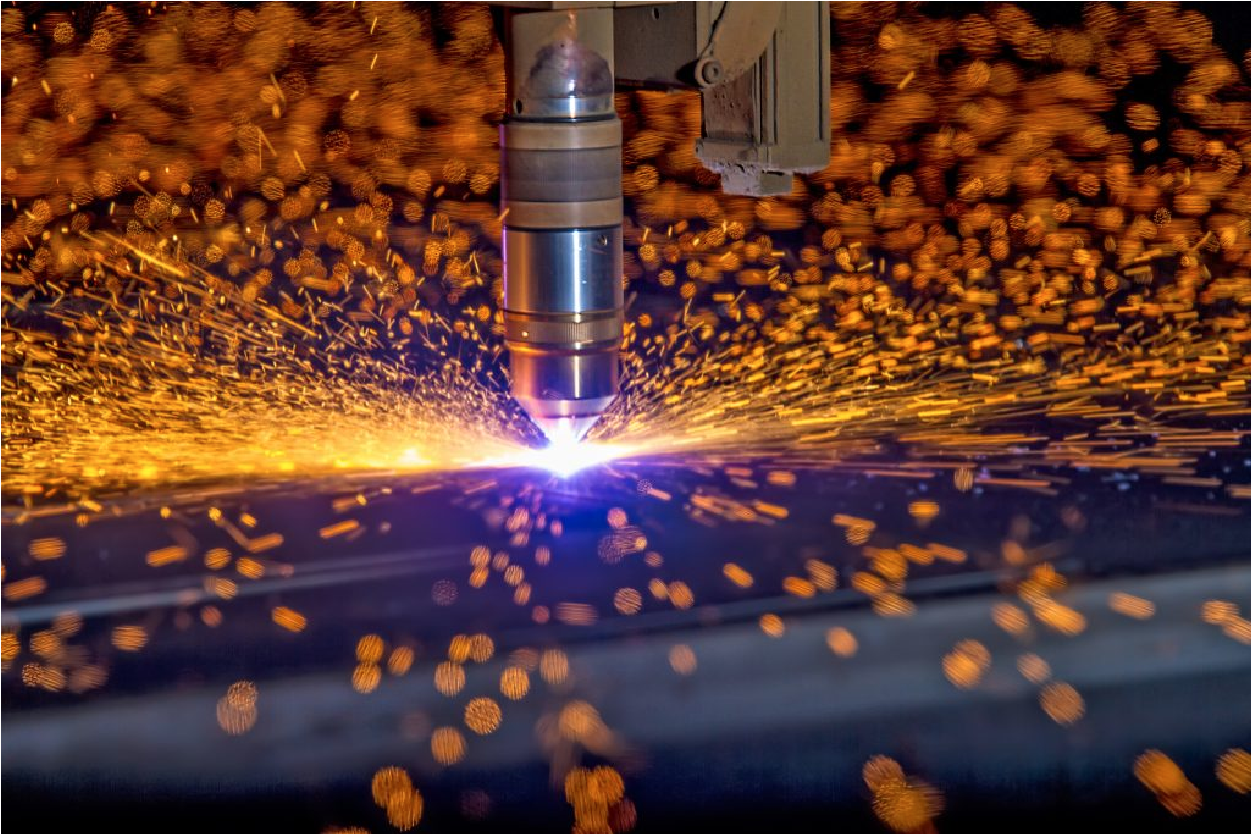
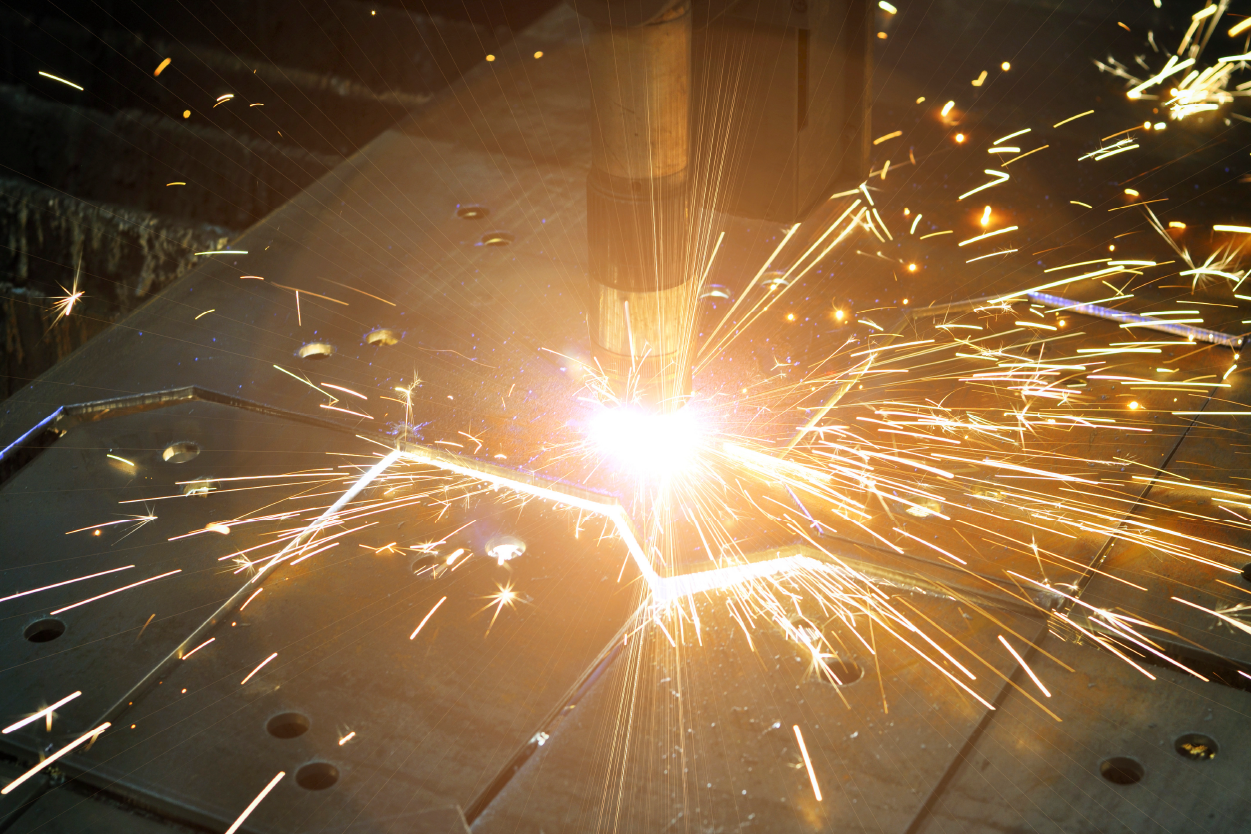
Plasma cutting is an efficient and versatile metal cutting process using a concentrated, high-temperature plasma arc to cut through various metal materials swiftly. This advanced technology also enables precise, clean, and rapid cutting of steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and other conductive metals, making it a popular choice for various industrial applications. This article will offer an overview of plasma cutting, including its operation, applications, and advantages.
How does it work?
Plasma cutting is a versatile and highly effective metal-cutting process that utilizes the power of ionized gas to cut through a wide range of materials precisely. But how exactly does this technology work?
At its heart is a plasma torch that constricts an electrical arc and focuses it through a fine-bore copper or silver nozzle. This high-energy arc ionizes the surrounding compressed air or gas, turning it into plasma—an electrically conductive state of matter hotter than the sun’s surface.
Moreover, as this superheated plasma jet is forced through the small nozzle, it develops tremendous cutting power; as a result, it can effortlessly slice through steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and other metals up to several inches thick. Consequently, the focused, high-velocity plasma stream melts and blows away the metal, leaving a precise, narrow kerf (cut width) with a minimal heat-affected zone.
Overall, it offers numerous advantages over traditional metal-cutting methods. Its speed, accuracy, and ability to cut thick materials make it an indispensable tool for various industries. From fabrication and construction to automotive and aerospace manufacturing, plasma cutting is invaluable. With the right plasma-cutting system, manufacturers can achieve superior results and greater productivity on even the most demanding metal-cutting projects.

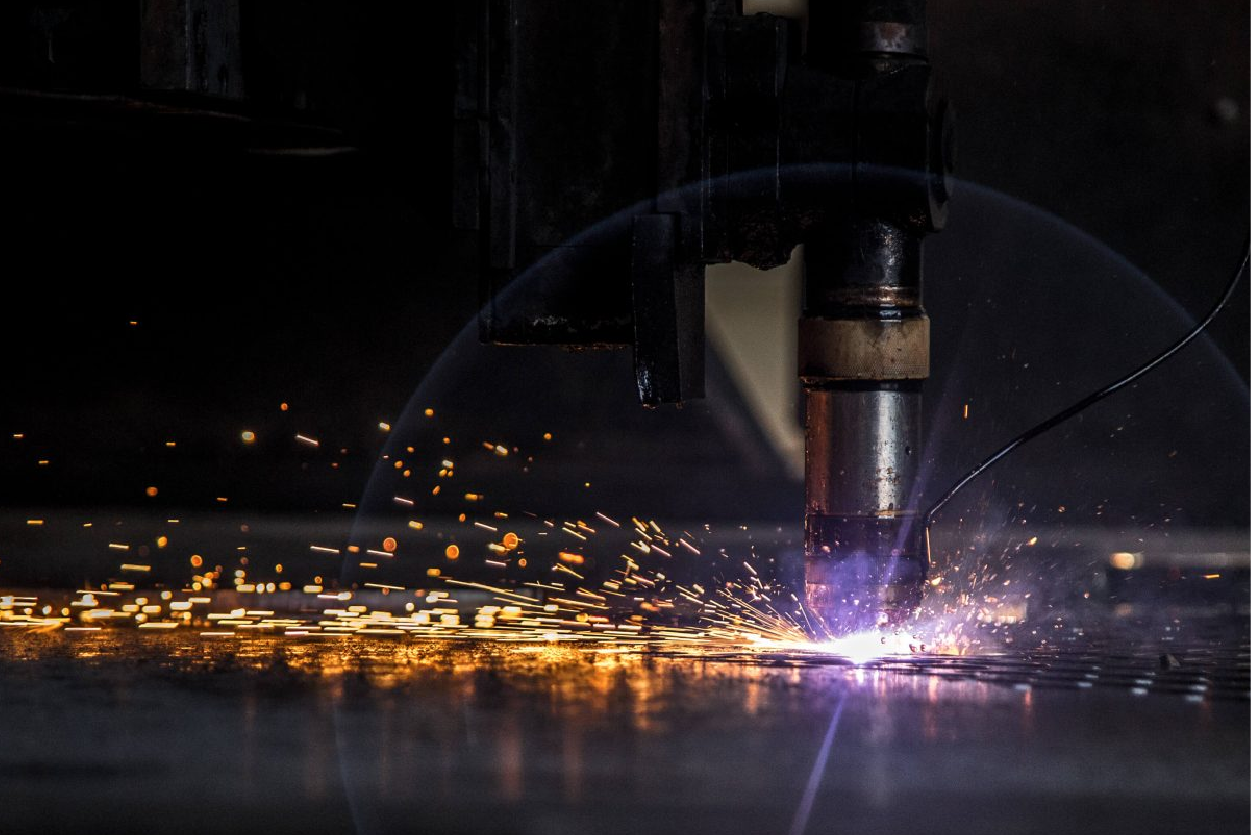
Plasma Cutting Applications
Plasma cutting is a highly versatile and efficient metal-cutting process that utilizes a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to melt and expel material, resulting in clean and precise cuts. Various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, use it due to its ability to offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for cutting steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
Moreover, one of its critical advantages is its capability to handle thick materials, making it an essential tool for cutting metal with varying thicknesses. This process is particularly advantageous for manufacturers, fabricators, and metalworkers because it can cut intricate shapes, bevel edges, or separate significant metal components with high speed and precision. Furthermore, the flexibility of plasma-cutting technology allows it to meet diverse production needs, making it a preferred choice for many applications across different industries.

Advantages of Plasma Cutting
First and foremost, this technology offers unparalleled precision, allowing for the achievement of intricate and complex designs with remarkable accuracy.
Moreover, the speed and efficiency of plasma cutting make it a game-changer in the manufacturing world. With its ability to cut through various metals quickly and consistently, production processes can be streamlined, ultimately boosting overall productivity.
In addition, it is a versatile technique that can handle various materials, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and non-metallic materials.
Furthermore, plasma cutting is more cost-effective than traditional cutting methods. The process is highly efficient, reducing material waste and minimizing the need for post-processing, ultimately saving time and money.
Finally, it is essential to note that it is a clean and environmentally friendly fabrication method. The process generates minimal fumes and emissions, making it a sustainable choice for eco-conscious businesses.
At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we harness the power of this technology to deliver exceptional results for our clients. Contact us today to learn more about how our advanced manufacturing capabilities can transform your next project.
Is plasma cutting right for my parts?
Plasma cutting is an incredibly versatile and efficient manufacturing process ideal for various parts. Additionally, our skilled team can assess your needs and offer expert advice on whether it is the best solution. Furthermore, we will consider material, thickness, complexity, and production volume to suggest the most appropriate manufacturing method. Please get in touch with us today to discuss your project and learn how our plasma-cutting capabilities can deliver high-quality, cost-effective results.
Are you ready to start your project?
FAQs
It is an exact and efficient metal-cutting process that uses a concentrated, high-temperature plasma arc to rapidly cut through various metal materials.
It is a highly efficient metal-cutting process that uses a concentrated, high-temperature plasma arc to melt and vaporize material rapidly. The plasma arc’s intense heat and speed allow for precise, clean cuts through a wide range of metals, making it a versatile manufacturing solution.
This versatile technology can handle various materials, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It offers precise, clean cuts on both thin and thick workpieces.
Plasma cutting is a versatile manufacturing process utilized across diverse industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and metal fabrication. It enables the precise and efficient cutting of a wide range of materials.