Teflon is a remarkable synthetic material that has revolutionized countless industries and significantly impacted our daily lives. Initially developed in the 1930s by scientists at DuPont, this versatile fluoropolymer is now essential in a wide range of products, including cookware, aerospace applications, and even medical devices. This blog post will delve into the intriguing history, unique properties, and various uses of this remarkable material, which has become a fundamental part of modern manufacturing and our daily lives. Furthermore, we will explore how Teflon’s unique characteristics have made it a preferred choice across different sectors. Understanding Teflon’s role ultimately helps us appreciate the technological advancements that have shaped our world.
What is the history of Teflon, and how is it made?
Roy Plunkett, a chemist working for DuPont, discovered Teflon in 1938. This accidental discovery, made while Plunkett was experimenting with refrigerant gases, created a slippery, waxy solid highly resistant to heat, chemicals, and corrosion. It marked a significant milestone in materials science, leading to the development of Teflon as we know it today.
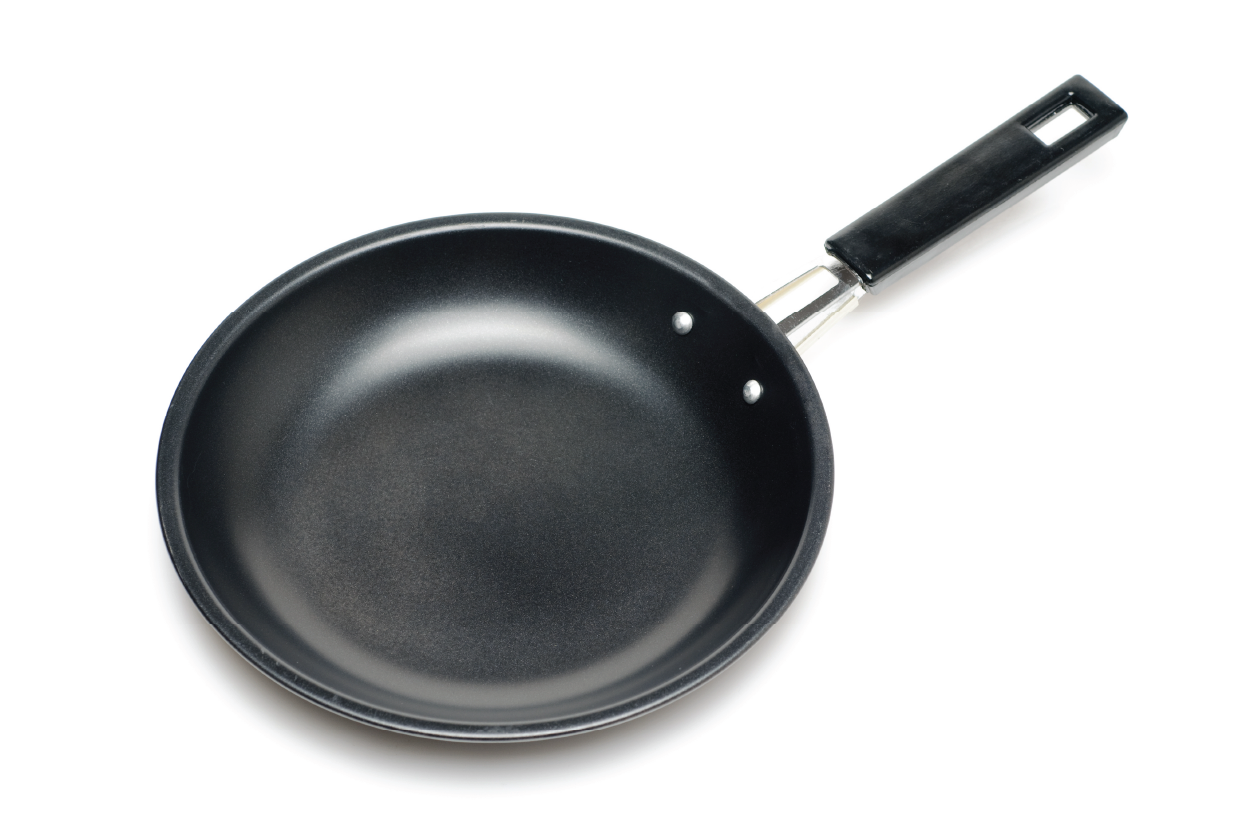
This revolutionary discovery led to the development of Teflon, which DuPont patented in 1941. Due to its unique properties, Teflon was initially primarily used in the aerospace and military sectors. However, it soon entered the consumer market and became a staple in kitchens worldwide as a nonstick coating for cookware.
The manufacturing process of Teflon is complex and involves several steps. First, the raw material, tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), is polymerized under high pressure and temperature to create Teflon resin. This resin is then extruded or molded into the desired shape, such as sheets, rods, or coatings.
The process of creating Teflon-coated cookware involves several steps. The first is applying sanding or roughening to the metal surface to enhance adhesion. Then, the resin was used in multiple layers, each baked at high temperatures to bond it to the surface. This meticulous process ensures that the Teflon coating is durable and long-lasting. Which provides the nonstick properties that Teflon is famous for.
Teflon’s versatility is evident in its use across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and healthcare. Its unique properties—such as nonstick, low friction, and chemical resistance—make it vital in countless products.
What are the mechanical properties of Teflon?
Teflon, known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a highly renowned material for its exceptional mechanical properties. Here are some key mechanical characteristics of Teflon:
High Tensile Strength: Its tensile strength ranges from approximately 20 to 30 MPa, making it a strong and rigid material suitable for various applications.
Low Coefficient of Friction: It is famous for its extremely low coefficient of friction, which allows for smooth and effortless movement between surfaces in contact. This property makes Teflon an excellent choice for bearings, seals, and other sliding components.
Excellent Wear Resistance: Thanks to its low friction and nonstick properties, Teflon exhibits exceptional wear resistance, maintaining its performance even under high-stress conditions.
High Chemical Resistance: Teflon is highly resistant to various chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents, making it suitable for harsh environments.
Thermal Stability: It can withstand temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) without significant degradation, making it ideal for high-temperature applications.
What industries use Teflon?
Teflon, the renowned nonstick coating, has become integral to numerous industries, revolutionizing how we approach various products and applications. With its exceptional properties, this remarkable material has found its way into multiple sectors, each benefiting from its unique characteristics.
Firstly, the cookware and bakeware market is a primary industry heavily reliant on Teflon. Its nonstick properties make it an indispensable choice for pots, pans, and baking sheets. These properties ensure effortless food release and easy cleaning, significantly improving food preparation efficiency and convenience in commercial and residential kitchens.
In addition to the culinary realm, Teflon has also made its mark in the automotive industry. Its low friction and heat-resistant qualities make it ideal for various automotive components, such as engine parts, brake systems, and gears. As a result, this material helps improve vehicles’ overall performance, efficiency, and longevity.
Moreover, the aerospace industry is another sector that heavily utilizes Teflon. Its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and chemical exposure makes it a crucial material for aircraft components, including seals, gaskets, and even the protective coatings on spacecraft. Thus, Teflon’s versatility ensures the safety and reliability of these critical systems.
Furthermore, this material is used in implants, and even medical tubing use this material in t Its nonstick property in the medical fields and biocompatibility make it ideal for devices that contact delicate tissues or bodily fluids, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
Notably, Teflon’s versatility extends even further. It is used in the construction industry as waterproofing and weatherproofing materials and in the textile industry as stain-resistant and water-repellent fabrics.
In conclusion, as industries evolve and seek innovative solutions, Teflon remains a reliable and adaptable material, transforming how we approach various products and applications. Its unique properties have made it an indispensable component in numerous sectors, driving progress and enhancing the overall quality and performance of the goods and services we rely on.
What are the benefits of using this material for your project?
Teflon is a versatile material that offers numerous benefits for your manufacturing projects. Its exceptional nonstick properties make it ideal for applications where easy release and minimal surface adhesion are crucial. This material’s chemical inertness and corrosion resistance ensure long-lasting performance, even in harsh environments. Additionally, this material’s low coefficient of friction can enhance the efficiency and smoothness of your components. Whether you’re working on additive manufacturing, CNC machining, or sheet metal fabrication, Teflon can be a valuable asset to your project.
FAQs
It is a durable, non-stick coating used in various products.
It is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, chemical processing, and food processing due to its exceptional non-stick and heat-resistant properties.
Exceptional durability, non-stick properties, and chemical resistance.
Doesn’t easily stick to substrate and poor radiation resistance.