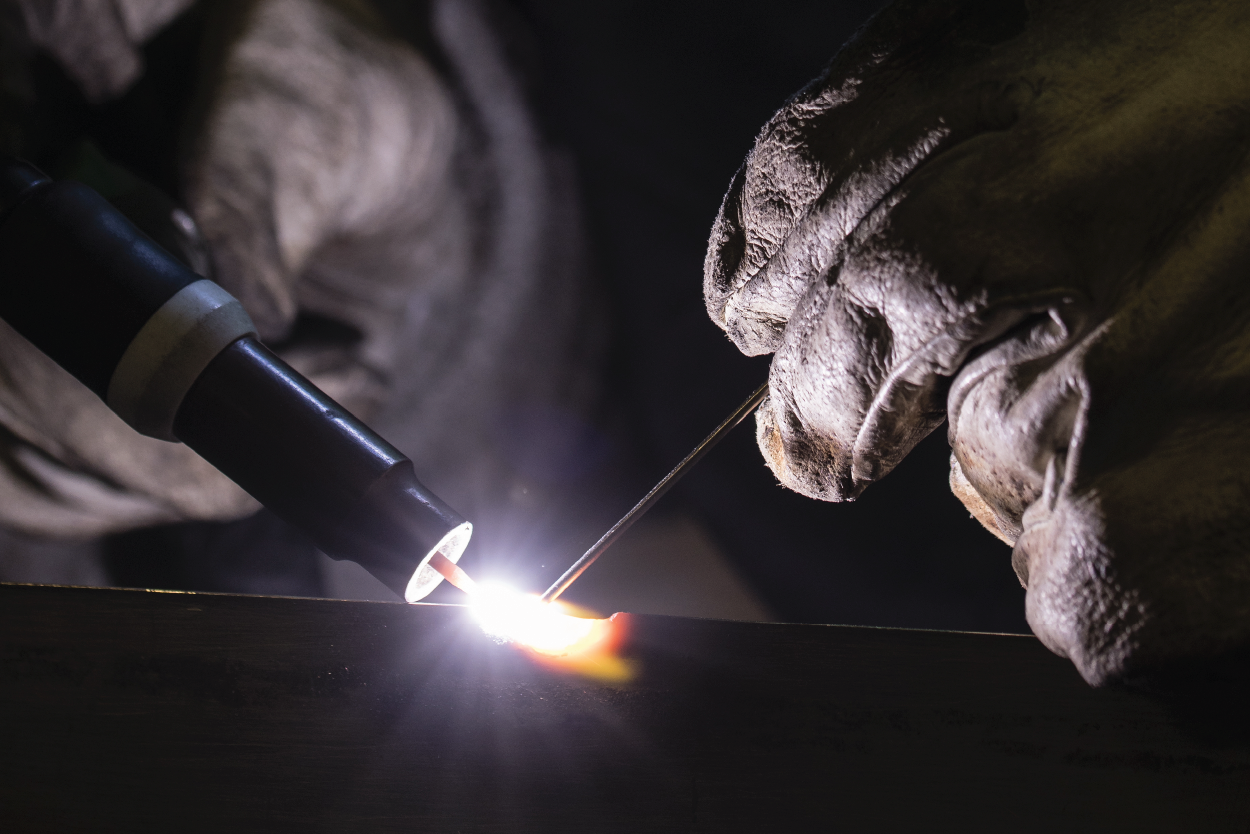
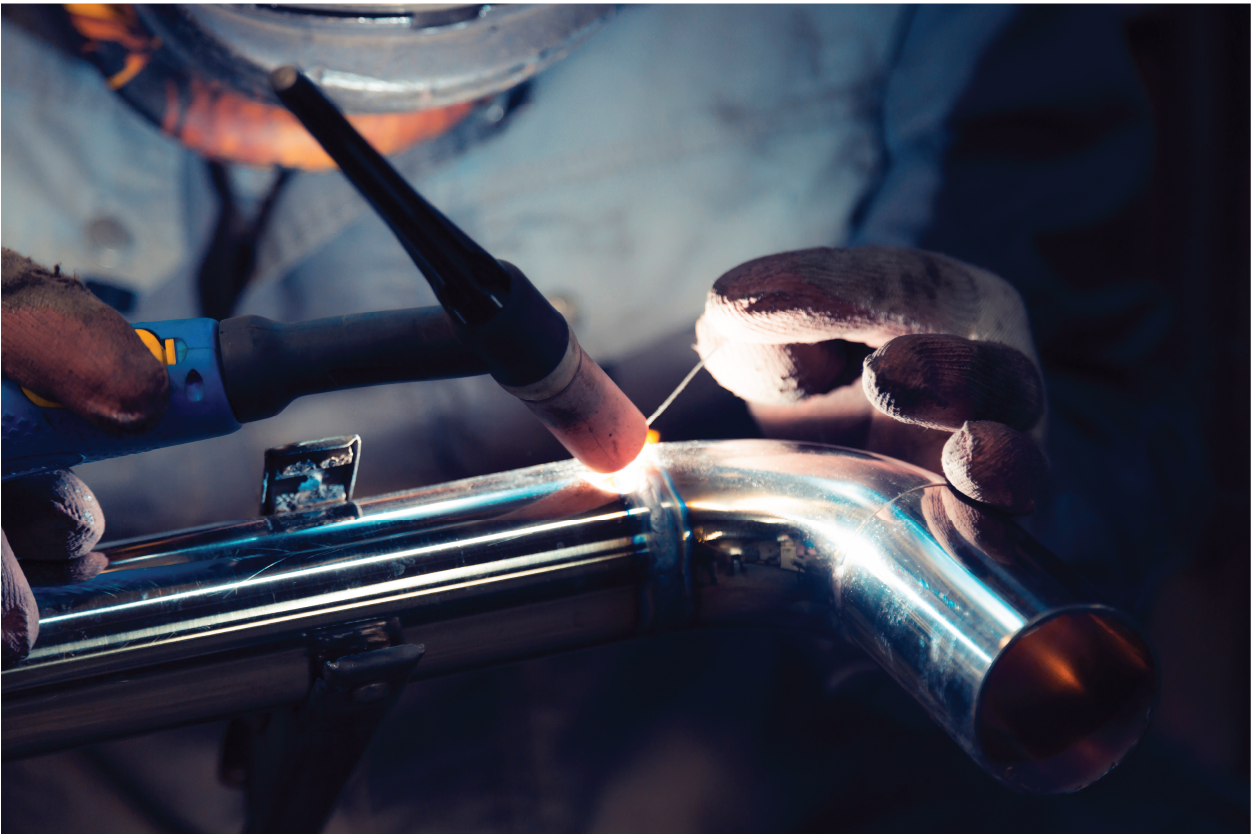
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, a method renowned for its precision and control, is a cornerstone in the toolkits of various industry fabricators, manufacturers, and metalworkers.
This post will explore the versatility and main advantages of TIG welding, which has become indispensable in modern metal fabrication.
How does the TIG process work?
TIG welding is a precise method for making strong and clean welds on various metals. It requires a steady hand and sound techniques. The following steps will delve into both preparation and welding.
Preparing to Weld
Grab Safety Gear
Before embarking on any welding project, ensure you have the proper protective gear. This gear includes shielding eyewear, thick fire-resistant clothing, and a helmet made explicitly for welding with an eye shield.
Connect the TIG Torch
The torch features an argon ceramic nozzle, a copper sleeve for holding the electrode, and a cooling system.
Plug in the Foot Pedal
Connect the foot pedal to the machine. This pedal controls the heat while you weld.
Choose the Polarity
Choose the right setting based on the metal you are welding. For aluminum, use alternating current (AC). Switch to DC Electrode Negative (DCEN) for steel or other metals.
Grind the Tungsten Rod
The thickness of the metal and the welding current affect how you should grind the tungsten rod. Instead of grinding it straight towards the ends, grind it in a circular motion around the outside edge.
For alternating current (AC) welding, shape the tungsten tip into a ball. For direct current (DC) welding, make the tip pointed. If you need to do a butt weld or an open corner weld, grind the tungsten to a length of five to six millimeters.
The Gas Flow Set-Up
Use pure argon gas or a mixture of argon and helium. Remove the plastic cap from the gas cylinder.
Next, open and close the valve quickly to remove any debris. Then, screw the regulator onto the valve and tighten it until it feels secure.
Use a spanner to tighten the regulator more, and make sure to turn the pressure knob counterclockwise to release pressure. Attach the gas hose and flowmeter. Open the cylinder valve slowly; a quarter turn is usually enough.
Finally, check for leaks by listening for a wheezing sound or using a leak detector spray.
Set the Gas Flow Rate
Adjust the cylinder regulator to set the gas flow. Although it can vary by each project, it usually stays between four and 12 liters (3.2 US gallons) per minute.
Set the Amperage
Amperage controls the welding process. If the material is thicker, a higher amperage is necessary. The more skilled welders get, the more they can increase their amperage with the foot pedal.
These are some common current ratios:
- 1.6 mm: 30 to 120 amps
- 2.4 mm: 80 to 240 amps
- 3.2 mm: 200 to 380 amps
Welding Steps
Clean Your Welding Material
Start by making sure your surface is clean and free of debris.
- Use a grinder or sander to polish carbon steel until it is bare and shiny.
- For aluminum, use a stainless steel wire brush.
- Clean the welding area with a solvent on a stainless steel rag, then stow away the rag and chemicals before welding.
Insert the Tungsten Electrode
Unscrew the back of the holder, insert the electrode, and then screw it back on. The electrode should stick out about 1/4 inch from the protective sheath.
Clamp the Pieces Together
Use an angle iron or flat bar with C-clamps to fasten the pieces you want to weld.
Tack Weld the Pieces Together
Make small tack welds where the metals meet every few inches to hold the parts in place until you can complete the final weld.
Hold the TIG Torch
Hold it at a 75-degree angle, keeping the tungsten 1/4 inch above the metal. Do not touch the workpiece, as this will contaminate it.
Practice Using the Foot Pedals
Use the foot pedals to control the heat. Your weld puddle should be about 1/4 inch wide. Keep the puddle size consistent to achieve a suitable finish.
Pick Up the Filler Rod
Hold the filler rod in your other hand, level with the workpiece at a 15-degree angle from the base where the torch heats.
Use Your Torch to Heat the Base Metal
The arc’s heat will create a puddle. This pool of molten metal fuses the two pieces.
Once you see a puddle on both pieces, tap the filler rod into the puddle quickly to prevent clumping. The filler material adds strength to your weld.
Advance the Puddle in the Desired Direction
Push the molten puddle away from the torch while TIG welding. Keep moving the puddle until you have welded the area you want to cover. Then, you will have finished your TIG weld!

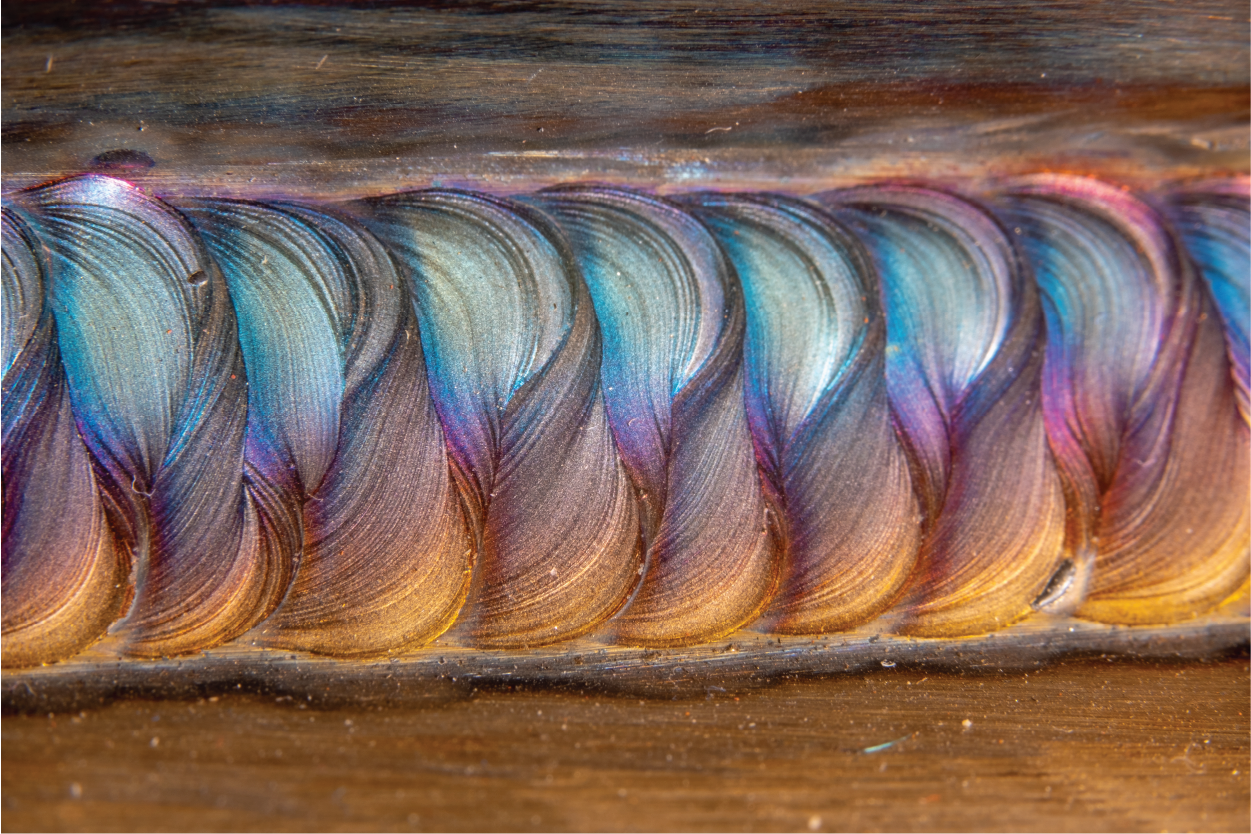
What materials can be TIG welded?
TIG welding, or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding gtaw, is a great choice for welding different materials. This method provides excellent control and produces high-quality, clean welds. At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we use TIG welding to join various metals, including:
Aluminum
This process’s precise heat control makes it ideal for welding aluminum, which has a lower melting point than steel.
Nickel Alloys
Specialized nickel alloys can also be successfully TIG welded, making this process a go-to for many industrial applications.
Stainless Steel
This welding process is an excellent choice for stainless steel, producing solid and corrosion-resistant welds.
Titanium
Titanium is challenging to weld, but this process allows for the control needed to create high-quality titanium welds.
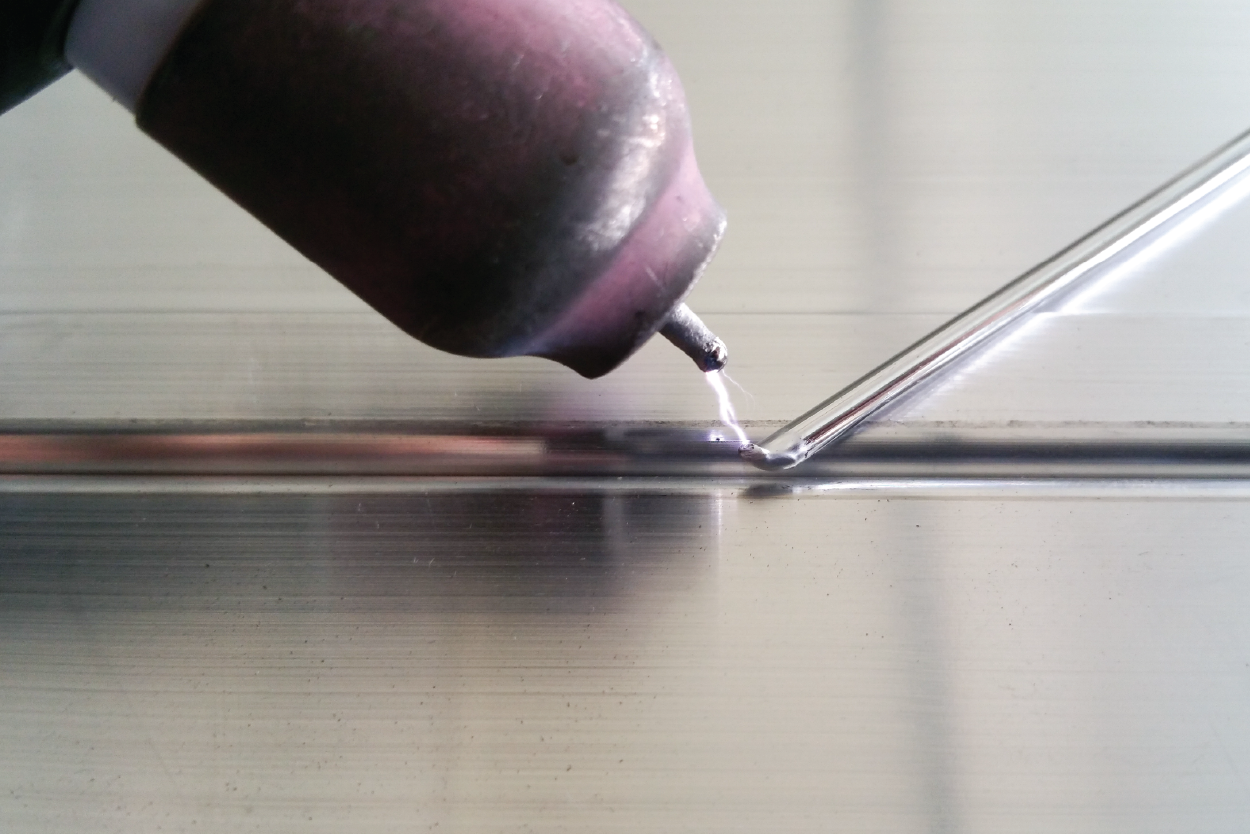
What are the benefits of TIG welding?
TIG welding is a well-respected method that benefits manufacturers in various industries. At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we use this technique to provide excellent results for our clients. This section will examine the advantages of this welding method and explain why it might be the right choice for your manufacturing needs.
Exceptional Weld Quality
TIG welding is known for its high-quality results. It creates clean, strong welds with minimal distortion and a smooth finish. Its precise control ensures consistent and reliable outcomes, making it a preferred choice for critical applications.
Versatility and Precision
With its versatility and precision, this welding method delivers high-quality results across various metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and exotic alloys. Its precise heat and filler metal control allow for detailed welds, making it ideal for complex parts and assemblies.
Enhanced Aesthetics
TIG welds look clean and professional, making them an excellent choice for projects where appearance matters. This welding method is critical in the automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods industries.
Improved Efficiency
This welding process is efficient. It reduces material waste and the need to finish after welding. This joining method can save you money and speed up your manufacturing projects, reassuring you about their cost-effectiveness.
Increased Productivity
In summary, precise control and consistent results can make your manufacturing processes more efficient, leading to higher productivity and less downtime.
At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we provide high-quality manufacturing solutions, including the benefits of TIG welding. Contact us today to learn how our TIG welders can help you meet your project goals.

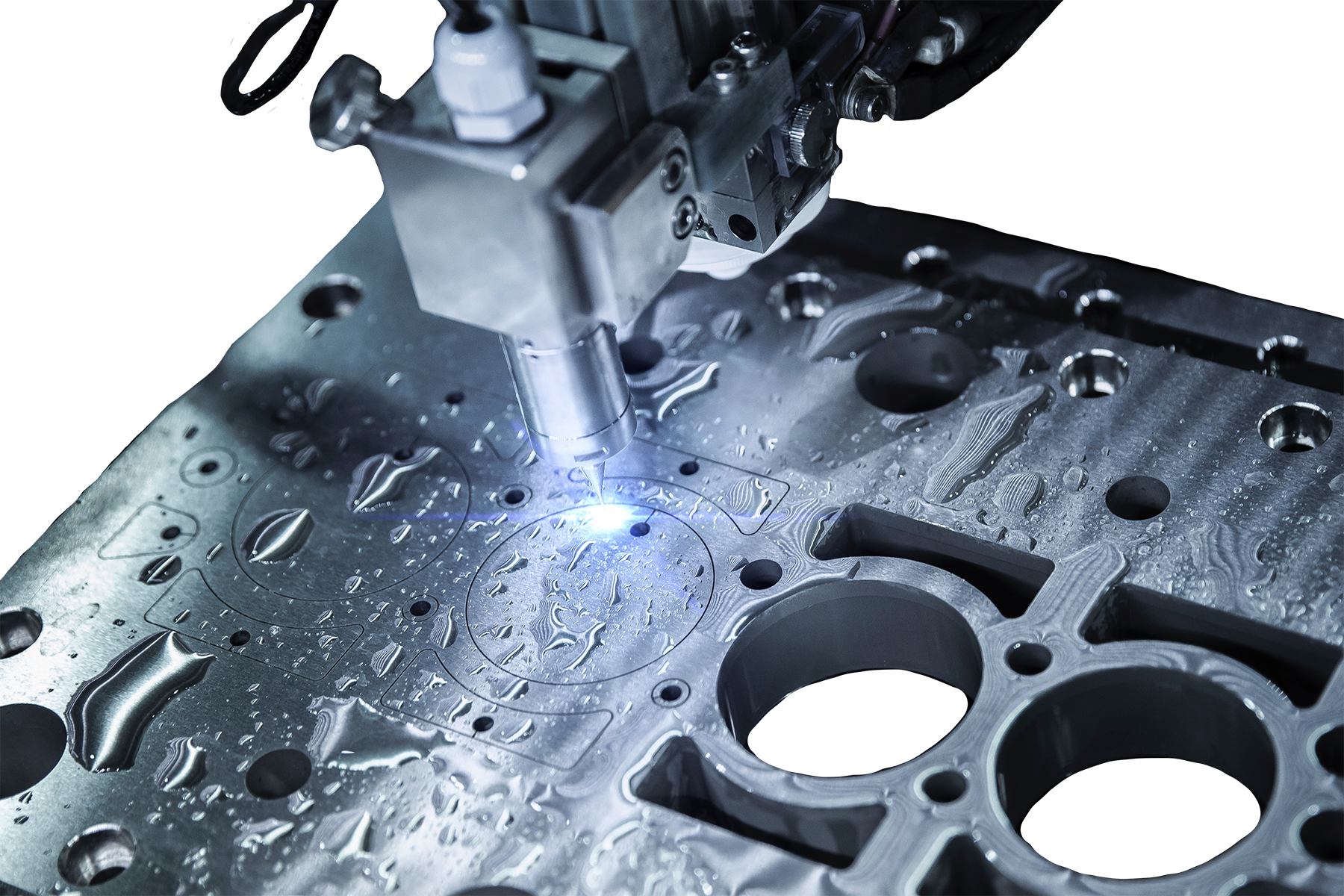
Why choose this method of welding for your project?
TIG welding is an excellent choice for your project due to its precision, controllability, and versatility. It produces focused heat, enabling high-quality welds on materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and exotic alloys. This adaptability allows you to achieve excellent weld quality and appearance with various materials. Our skilled TIG welding experts are ready to help you achieve the flawless results you desire.
CNC Machine Shop Services
Prototek offers state-of-the-art CNC machining services to meet your precise manufacturing needs. Our skilled technicians utilize the latest CNC technology to deliver high-quality components with unparalleled precision and efficiency—Trust Prototek for all your CNC machining requirements.

Sheet Metal Fabrication Services
At Prototek, we offer comprehensive sheet metal fabrication services to meet your manufacturing needs. Our skilled team utilizes the latest technology and techniques to deliver high-quality, precision-engineered components. From prototyping to production, trust Prototek to bring your ideas to life.
FAQs
It is a precise and versatile welding process that produces high-quality, clean, and strong welds.
This versatile welding process can join various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and nickel-based alloys.
Aerospace, automotive, shipbuilding, and commonly use it for stainless steel and aluminum components fabrication.
The main welding methods include MIG, TIG, Laser Welding, and Arc Welding, each with unique characteristics and applications.
In TIG welding, the shielding gas protects the weld pool and the electrode from atmospheric contamination, ensuring a high-quality, consistent weld.