Titanium is a strong and lightweight metal with unique corrosion resistance. Its exceptional properties have made it indispensable in various manufacturing sectors, including aerospace and medical implants, sparking intrigue and fascination among professionals worldwide.
This blog post will examine titanium’s history, uses, and why many industries prefer it as a material.
What is titanium?
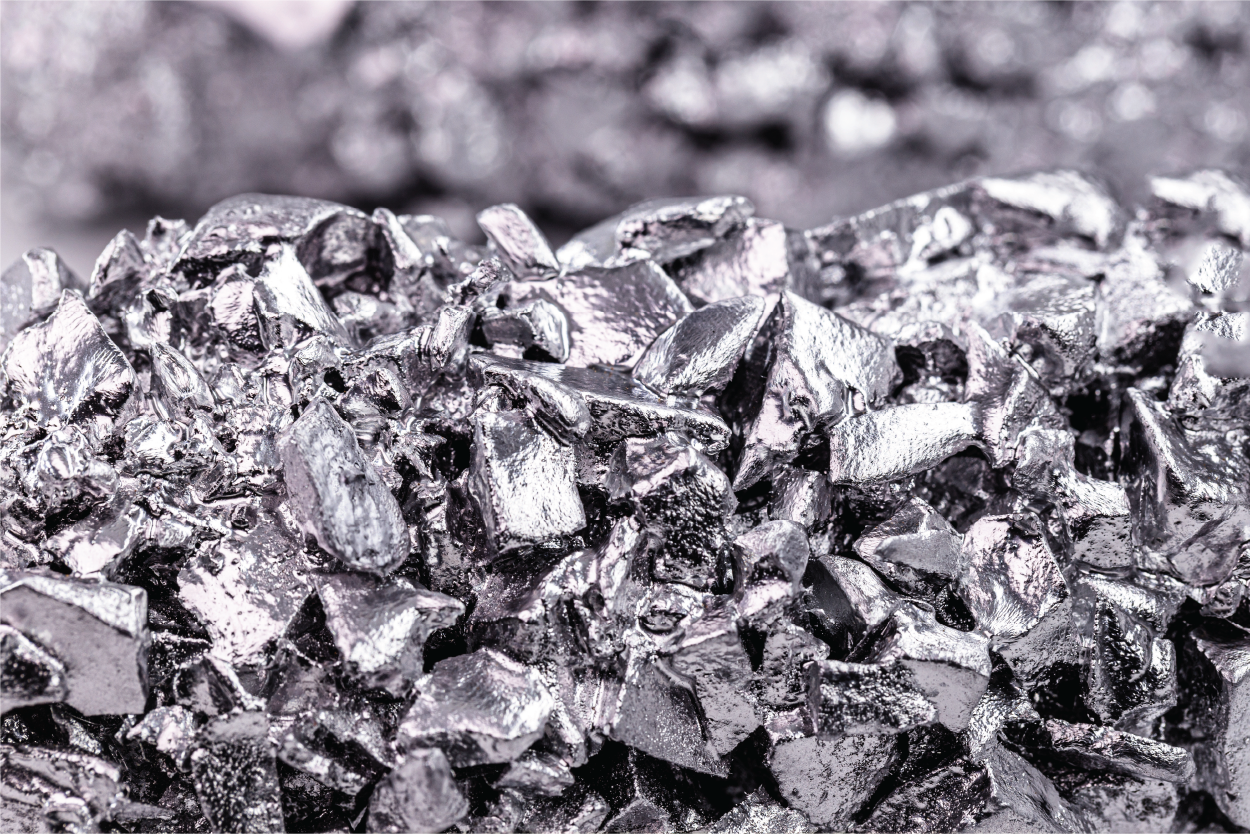
Titanium is a strong and lightweight metal that does not rust. Many industries use it because it is both strong and light. This metal is a top choice for industries where low weight and high durability are vital, such as aerospace, medical devices, and sports equipment.
Titanium has the atomic number 22 and the chemical symbol Ti. It is a transition metal on the Periodic Table of Elements and the earth’s ninth most abundant element. Transition metals can change their oxidation states because of their partially filled d orbitals, which allows them to form ions with different charges. They are known for forming colored compounds, having high melting points, and often serving as catalysts. Depending on the reaction, they can quickly gain or lose electrons.
Titanium is a shiny metal that appears silvery and can range in color from gray to white. It is never in its pure form in nature due to its reaction with oxygen. It comes from minerals found in igneous rocks, sedimentary deposits, beach sands, and metamorphic rocks. While it is not the most expensive metal for manufacturing, it does cost more than aluminum and steel. Its strength, low thermal conductivity, and chemical reactivity make it challenging to fabricate and machine.
Its unique properties ensure it performs well, making titanium a valuable material in manufacturing and engineering.

What is the history of titanium, and how was it made?
The history of Titanium is a captivating journey that dates back to the early 19th century. In 1791, English chemist William Gregor serendipitously discovered this remarkable metal while studying the mineral ilmenite, laying the foundation for its future. Fast-forward to 1910, American chemist Matthew Hunter achieved a significant milestone by producing pure Titanium for the first time, a pivotal moment in the metal’s history that connects us to its past.
Today, we produce Titanium using the Kroll process, a method developed by William Kroll in the 1930s. This process starts with mining and refining titanium ores like rutile or ilmenite. It also involves purifying liquid titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) and converting the ore into this compound. The result is a titanium sponge, which is melted and shaped into ingots or other forms for use in various products.
Its unique and fascinating qualities make it robust yet lightweight, impervious to corrosion, and biocompatible. These exceptional attributes have rendered this metal indispensable in many industries, from aerospace and defense to medical and consumer goods. The sheer versatility of Titanium, driven by these benefits, inspires innovation and technological progress across various fields.
What are the mechanical properties of titanium?
Titanium is a strong metal that many industries rely on for its critical mechanical properties.
Biocompatibility and Osseointegration
Titanium is often used in medicine for implants, dental fixtures, and other devices because it works well with the body. A unique feature of this material is its ability to bond with bone tissue, a process called osseointegration. The implant becomes part of the body and forms a strong link with the bone, helping patients heal faster and improving their health.
Corrosion Resistance
Titanium also resists corrosion very well. It forms a thin, protective layer on its surface that protects it from chemicals, even in harsh conditions, making it a good choice for marine applications, chemical processing, and medical implants.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Titanium is strong yet lightweight. It is almost as strong as steel but 45% lighter, which is crucial when weight is essential. This strong-to-weight ratio helps make products for the aerospace, automotive, and medical fields.
Thermal and Cryogenic Resistance
Titanium remains strong and flexible in extreme heat and cold. Due to its ability to endure high and low temperatures, it is suitable for use in aerospace, energy, and industrial settings.

What types of titanium grades and alloys are popular?
Titanium is a strong and lightweight material used in many industries, such as aerospace, defense, medical, and consumer products. It is popular because it is safe for the body, does not rust, and is very strong for its weight.
Commercially Pure (CP) Titanium
CP titanium is the purest form, containing very few alloying elements. There are four grades (Grades 1-4) based on the levels of impurities and oxygen. People value CP titanium for its excellent corrosion resistance. Medical industry applications include medical implants, chemical processing equipment, and marine applications.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys improve their properties by adding small quantities of other elements such as aluminum, vanadium, molybdenum, or chromium. Furthermore, some of the most widely used alloys include:
Ti-6Al-4V
This titanium alloy is widely used due to its balanced combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and formability, making it prevalent in aerospace, medical, and industrial applications.
Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo
This alloy is known for its high strength and creep resistance, making it suitable for jet engine components and other high-temperature applications.
Ti-3Al-2.5V
This alloy is known for its excellent ductility and is often used to produce seamless tubing, hydraulic and fuel lines, and other applications where formability is crucial.
Ti-5Al-2.5Sn
Is known for its high strength, excellent resistance to creep, and superb weldability, making it a popular choice for aircraft engine components, rocket motors, and other aerospace applications.

Which industries use titanium, and what are some of its applications?
Titanium is an essential metal used in many industries around the world. It is strong, lightweight, and does not rust. Because of these qualities, this metal has many uses and has changed several fields. This section will examine the industries that use this versatile metal and its different applications.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry uses Titanium because it is strong and lightweight. Engineers use it for parts in planes and spacecraft, such as airframes, engines, and landing gear. Titanium can withstand extreme temperatures and resist corrosion, essential for aerospace conditions.
Automotive and Transportation
The automotive and transportation sectors use it for their properties. Applications such as suspension systems, exhaust components, and high-performance sports car components use this metal. Its strength and light weight help improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.
Consumer Goods and Lifestyle
Titanium is also popular in consumer products. Its strength, lightweight, and hypoallergenic properties make it ideal for high-end watches, jewelry, sporting equipment, and outdoor gear.
Industrial and Chemical Processing
Titanium is valuable in industrial and chemical processing. Its resistance to corrosion makes it suitable for equipment and piping in industries like power generation and desalination, and its strength allows it to handle harsh conditions in these settings.
Medical and Dental Applications
Titanium is a top choice in medicine and dentistry because it works well with the human body and does not rust. Doctors use it for dental implants, hip replacements, knee replacements, and orthodontic devices. Its ability to bond with the body makes it a preferred material for these uses.
In summary, Titanium is a versatile metal found in many industries. Its unique properties and wide-ranging applications are key in modern manufacturing and engineering.

What are the benefits of using this material?
Titanium is a high-value material with a strong and lightweight material that many industries use. Its strength-to-weight ratio gives it outstanding durability, making it perfect for applications that need strength and lightness. This metal is also very corrosion-resistant and works well in harsh environments like marine and chemical processing.
Medical implants and devices use Titanium because it is safe for the body. It can handle extreme temperatures, which expands its use across various fields. Its combination of these properties allows for many design possibilities, making it a go-to choice for innovative products in different sectors.

Why choose this material for your project?
Titanium is an excellent choice for your project because it is strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant. Prototek Digital Manufacturing uses Titanium to make high-quality parts that meet strict requirements. It offers a strong yet light design, if you need precise machined parts, custom castings, or advanced 3D printing solutions. Our team of experts is ready to help you make the most of this impressive material for your next project.
CNC Machine Shop Services
Prototek offers state-of-the-art CNC machining services to meet your precise manufacturing needs. Our skilled technicians utilize the latest CNC technology to deliver high-quality components with unparalleled precision and efficiency—Trust Prototek for all your CNC machining requirements.

Sheet Metal Fabrication Services
At Prototek, we offer comprehensive sheet metal fabrication services to meet your manufacturing needs. Our skilled team utilizes the latest technology and techniques to deliver high-quality, precision-engineered components. From prototyping to production, trust Prototek to bring your ideas to life.
FAQs
It is a strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant metal in various industries, including aerospace, medical, and consumer products.
This lustrous, silver-gray metal with a high strength-to-weight ratio makes it a popular choice in various industries.
It is a non-magnetic metal that is not attracted to magnetic fields. This unique property makes titanium popular for various industrial and medical applications.
This material is highly resistant to corrosion and does not rust. Its strong, durable, and lightweight properties make it a popular choice for various industrial and medical applications.
It is a highly reactive metal that readily forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to oxygen, making it resistant to corrosion.
It is indeed found on the periodic table and is classified as a transition metal with the atomic number 22. It is a strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant element.