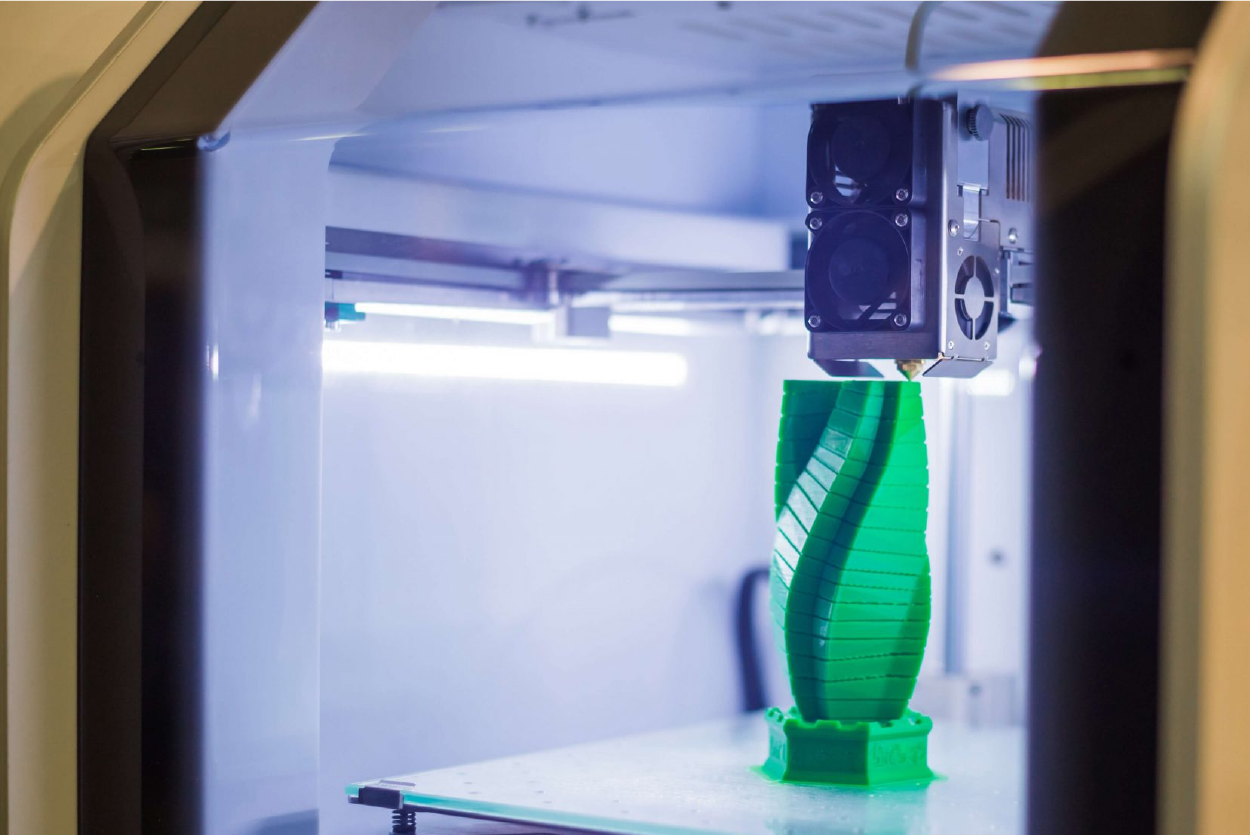
History of 3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has significantly revolutionized how we create and produce physical objects. This innovative technology has evolved dramatically since its inception and continues to impact various industries.
The roots of additive manufacturing can be traced back to the 1980s when Chuck Hull developed the first 3D printing system, stereolithography (SLA). This invention allowed for the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital files, marking the beginning of a new era in manufacturing.
Over the following decades, the technology advanced rapidly. New techniques such as fused filament fabrication (FFF), selective laser sintering (SLS), and digital light processing (DLP) were introduced. These advancements made 3D printing more accessible, affordable, and versatile, enabling the production of a wide range of products, from simple prototypes to complex, customized parts.
As technology evolved, 3D printing became widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods. Manufacturers began using additive manufacturing for benefits, such as producing complex geometries, reducing material waste, and speeding up product development.
Today, additive manufacturing has become an integral part of the manufacturing landscape. Improvements in materials, speed, and precision are driving its widespread adoption. From producing medical implants to creating personalized consumer goods, the possibilities of 3D printing continue to expand, shaping the future of manufacturing and design.
At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we take pride in being at the forefront of this technological revolution. Our state-of-the-art facilities and experienced team of experts are committed to helping our clients utilize the power of additive manufacturing to bring their ideas to life.

Hobbyist vs Industrial
3D printing has become an increasingly popular technology, with applications ranging from personal hobbies to large-scale industrial manufacturing. While the underlying principles are similar, there are distinct differences between hobbyist and industrial 3D printing that are important to understand.
Hobbyist 3D Printing
Hobbyist 3D printing is typically done on desktop-sized machines and is often used for personal projects. These printers are generally more affordable and accessible, making them an excellent option for individuals, small businesses, and educational settings. Hobbyist 3D printers offer many materials, including PLA, ABS, PETG, etc. The print quality can be excellent but may not always meet the tight tolerances required for industrial applications.
Industrial 3D Printing
Industrial 3D Printing, on the other hand, is used for large-scale, high-volume manufacturing. These printers are typically more extensive and powerful and capable of producing parts with tighter tolerances and higher precision. It often utilizes advanced materials like ceramics and high-performance polymers, allowing for the creation of durable, functional parts. The equipment and materials used in industrial 3D Printing are generally more expensive, but the output is tailored to meet the demands of commercial and industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Approach
When deciding between hobbyist and industrial 3D Printing, it’s essential to consider your specific needs and requirements. Hobbyist 3D printing may be better for personal projects. In contrast, industrial 3D Printing is better suited for prototyping, low to medium-volume manufacturing, mission-critical parts, and applications requiring tight tolerances and advanced materials.
3D Printing at Prototek
At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, we specialize in offering a wide range of industrial 3D printing services and various other professional manufacturing capabilities. Moreover, our dedicated team of experts is committed to helping you make informed decisions by providing personalized recommendations on the most suitable technologies and materials for your project. Whether guiding you through the initial stages or managing the entire process from start to finish, we are here to ensure that your project meets and exceeds your expectations.

3D Printing From Start to Finish
To better understand how additive manufacturing works from start to finish, in four steps:
- Design: This is the beginning of any additive manufacturing idea. Once the design has been finalized in a CAD program, it is typically exported as an OBJ, STL, or any file format that slicing software can understand and interpret.
- Slicing: This step turns the CAD model into a file format that a 3D printer can understand. The slicer creates a G-code file that has the commands for the printer to create the desired object. G-code tells the printer the exact coordinates for every move of the printer extruder. Slicer settings are usually the part of the 3D Printing process that requires the most tuning to obtain a high-quality print.
- Printing: The information from the G-code file is used by the additive manufacturing machine to build each layer. This step may look different for different printing methods, but the layer-by-layer AM process holds for each method.
- Post-processing: This step involves cleaning up the printed object. It can involve removing unnecessary support material or adding finishing touches like filler and paint. Due to the nature of the build method, some 3D Printing methods require more post-processing time than others.

Advantages of 3D Printing
Design Flexibility
3D printing allows for the creation of complex, customized designs that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
Rapid Prototyping
Its speed and efficiency enable businesses to quickly create prototypes, test designs, and iterate on ideas.
Cost-Effectiveness
3D printing can be more cost-effective for specific applications than traditional manufacturing, especially for small-scale production runs.
Reduced Waste
Additive manufacturing produces less waste than subtractive manufacturing processes, making it more environmentally friendly.
Personalization
3D printing enables the creation of personalized products, from custom medical devices to one-of-a-kind consumer goods.
Are you ready to start your project?
FAQs
It is also known as additive manufacturing, creates three-dimensional objects by building them up layer by layer. It allows for the production of complex and customized parts.
At Prototek Digital Manufacturing, our capabilities allow us to create various custom parts and products. The possibilities are endless, from functional prototypes and end-use components to intricate models and unique designs. Contact us to see if our advanced additive manufacturing technologies enable us to bring your ideas to life!
Additive manufacturing is useful across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, consumer goods, and industrial manufacturing. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for diverse applications.
At Prototek, we utilize an extensive and diverse range of materials specifically designed for industrial 3D printing, including thermoplastics, high-performance ceramics, and advanced composites. This wide selection enables us to produce high-quality, fully functional parts for many applications across different industries and sectors, ensuring durability and performance that meet our clients’ unique needs and specifications.
For more information, check out our AM Material Pro.