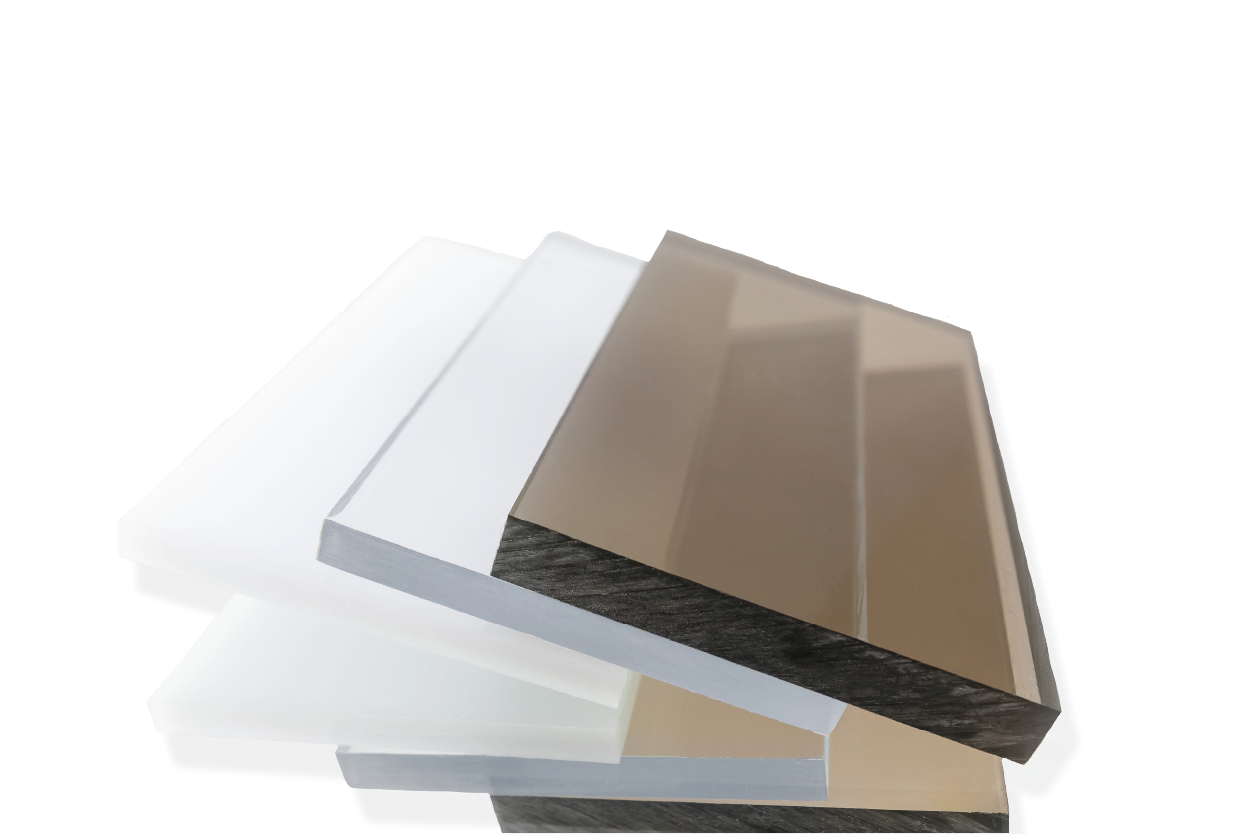
Polycarbonate is a versatile and durable thermoplastic material that has gained popularity in various industries. Discover its unique properties and uses. This blog post will explore its essential characteristics and how it can enhance your next project.
What is the history of Polycarbonate, and how is it made?
Polycarbonate, a versatile and durable thermoplastic material, has a rich history dating back to the 1950s. Developed by scientists at Bayer AG in Germany, it was first commercialized in 1958 under the trade name Makrolon, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of materials engineering.
Polycarbonate’s unique molecular structure gives it exceptional impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat resistance—properties that have made it an invaluable material across various industries. It has become essential to modern life, from eyeglasses to bulletproof windows and aerospace components.
The manufacturing process for polycarbonate begins with the reaction of bisphenol A (BPA) and phosgene under carefully controlled conditions. This step produces a resin, which can then be melted, extruded, and molded into various end products. Depending on the specific application, this material can be injected or extruded.
Thanks to continuous innovations in polycarbonate chemistry and manufacturing techniques, this versatile material continues to find new uses and applications. Prototek offers fabrication, machining, and additive manufacturing services to help bring our customer’s visions to life and contribute to the exciting future of polycarbonate applications.

What are the mechanical properties of Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonate is a widely used engineering plastic renowned for its exceptional mechanical properties. This thermoplastic material offers a unique combination of impact resistance, optical clarity, and strength, making it a popular choice in various industries.
One of polycarbonate’s most notable features is its high impact strength, which allows it to withstand significant impact and shock without shattering or cracking. Consequently, it is an ideal material for applications that require durability and safety. Additionally, its impact resistance contributes to its shatter-resistant qualities, which are critical for many end-use products.
In addition to its impact strength, polycarbonate exhibits impressive tensile strength, enabling it to withstand high stress levels and strain without deforming or breaking. It provides reliable structural integrity, allowing polycarbonate components to support heavy loads and resist deformation under pressure.
Furthermore, polycarbonate boasts excellent dimensional stability, maintaining its shape and size even under varying environmental conditions. Its thermal resistance enables it to perform well in a wide temperature range, from sub-zero to elevated temperatures. Thermal stability is advantageous for applications exposed to temperature extremes.
Due to its unique mechanical properties, polycarbonate remains preferred by engineers and designers across automotive, electronics, construction, and other industries. Its versatility and performance make it an invaluable asset in modern manufacturing.

Which industries use the material?
Polycarbonate is an exceptional engineering plastic with wide-ranging applications in various industries. This durable, transparent, and impact-resistant material offers a unique combination of properties, making it an essential choice for numerous applications and a versatile solution for many projects.
Polycarbonate in the Automotive Industry
Polycarbonate is a staple in the automotive industry, where it is used for headlamps, taillights, sunroofs, and other exterior components. Furthermore, its shatter-resistant nature and lightweight properties make it an ideal material for enhancing vehicle safety and fuel efficiency.
Electronics & Appliances
The electronics and appliances industry heavily relies on polycarbonate for housing, casings, and components. Its durability, impact resistance, and thermal stability make it a preferred choice for protecting sensitive electronic devices and ensuring long-lasting performance.
Construction & Architecture
Polycarbonate’s transparency and ability to withstand weathering conditions make it a popular choice for architectural applications, such as skylights, roofing panels, and building facades. Its versatility allows for the creation of innovative and visually striking structures.
Polycarbonate in the Medical & Healthcare Industries
Medical devices, surgical equipment, and protective gear are all components that can use polycarbonate in the medical and healthcare sectors. Furthermore, its biocompatibility and sterilization capabilities make it essential in producing life-saving and life-enhancing products.
Polycarbonate in Consumer Products
Polycarbonate’s versatility extends to the consumer goods industry, from eyewear to sports equipment. Its shatter-resistance and lightweight properties make it ideal for creating durable and safe products that enhance the user experience.
Polycarbonate’s unique properties have made it an indispensable material across various industries. Additionally, its ability to combine strength, transparency, and design flexibility has transformed the way we interact with the world around us.

What are the benefits of using Polycarbonate for your project?
Due to its remarkable properties, polycarbonate is an excellent material choice for a wide range of projects. Its high impact resistance, optical clarity, and thermal stability make it ideal for durability and performance applications. Its versatility allows for innovative design possibilities, while its ease of fabrication, machining, and additive manufacturing streamlines the manufacturing process. When you choose this material, you can expect reliable, long-lasting results that enhance the quality and functionality of your project.
FAQs
It is a durable, transparent thermoplastic material known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity.
The automotive, electronics, construction, and healthcare industries use it due to its durability, impact resistance, and optical clarity.
Various applications use it, including eyewear, electronics, automotive parts, and construction materials.
Finishing these components with various methods, including painting, plating, and coating, enhances their appearance and durability.